In today’s world, people are increasingly health-conscious, particularly when it comes to beneficial bacteria (probiotics). Many focus on consuming foods rich in probiotics and prebiotics, but another key component is now gaining attention: postbiotics. These substances play an important role in supporting health and are becoming increasingly popular.
What Are Postbiotics?
Postbiotics are bioactive compounds produced during the metabolic processes of probiotics, the beneficial bacteria that live in our gut. When these bacteria consume food (prebiotics) and undergo metabolism, they release various substances, such as:
- Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), including butyrate, acetate and propionate
- Enzymes
- Proteins and peptides
- Antimicrobial compounds such as bacteriocins
- Vitamins, including B vitamins and vitamin K
- Organic acids
These substances provide health benefits without needing live bacteria, unlike probiotics.
How Do Postbiotics Differ From Probiotics and Prebiotics?
- Probiotics: Live microorganisms that are beneficial to health, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, which help maintain gut balance.
- Prebiotics: Dietary fibres or nutrients that serve as food for probiotics, such as inulin and fructooligosaccharides (FOS).
- Postbiotics: Bioactive substances generated from probiotic metabolism, including SCFAs, vitamins and enzymes, which offer health benefits without relying on live microorganisms.
Key Benefits of Postbiotics
- Support gut health: Enhance the function of beneficial gut bacteria and inhibit harmful bacteria.
- Reduce inflammation: Possess anti-inflammatory properties within the gut.
- Strengthen the immune system: Help support and regulate immune function.
- Assist in managing blood sugar and weight: SCFAs can reduce appetite and help regulate blood glucose.
- Enhance nutrient absorption: Provide nutrients that the body can utilise directly.
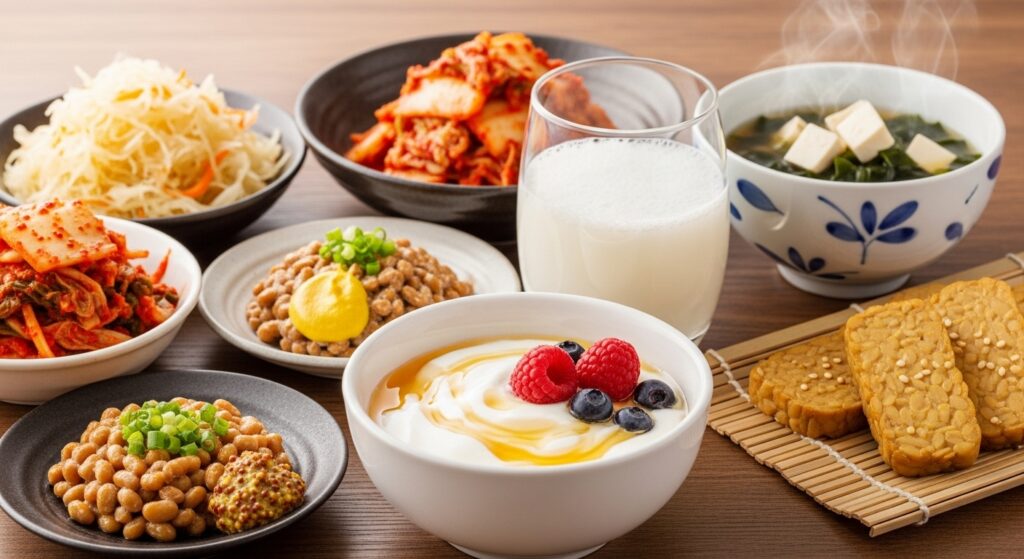
Food Sources of Postbiotics
Although postbiotics are widely available as supplements, they can also be obtained from natural food sources such as:
Yoghurt and kefir: Rich in SCFAs and health-supporting enzymes.
- Natto: A good source of vitamin K2 and antioxidants.
- Kimchi and sauerkraut: Contain lactic acid, which promotes gut health.
- Miso and tempeh: Provide essential proteins and amino acids.

References
1.Collado, M. C., Endo, A., Hill, C., Lebeer, S., Quigley, E. M. M., Sanders, M. E., Shanahan, F., & Salminen, S. (2021). The ISAPP consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 18(9), 649–667.
2.Rafique, N., Hassan, A., & Imran, M. (2023). Promising bioactivities of postbiotics: A comprehensive review. Food Research International, 172, 113098.
3.Vinderola, G., Sanders, M. E., Salminen, S., & Szajewska, H. (2022). Postbiotics: Concept and their use in healthy populations. Frontiers in Nutrition, 9,
4.Zdybel, K., Nowak, M., & Kowalska, J. (2025). Postbiotics formulation and therapeutic effect in inflammatory conditions. Nutrients, 17(13), 2187.