What is Diabetes Mellitus (DM)?
Caused by a malfunction of the hormone called insulin or insulin resistance. Consequently, the normal process of absorbing blood sugar to produce energy in the body’s cells becomes abnormal, leading to accumulation of sugar in the bloodstream.”
Causes of diabetes :
Caused by the level of sugar in the bloodstream rising to a certain level until it causes the kidneys to not absorb all the sugar back. Normally, the kidneys are responsible for reabsorbing sugar from substances filtered from the glomerular unit, resulting in sugar coming out of the urine which is the origin of the word diabetes.
This condition occurs when the sugar levels in the bloodstream become elevated to a certain extent, leading to impaired kidney function in filtering out the sugar. Normally, the kidneys are responsible for reabsorbing sugar from substances that pass through them. Consequently, the excess sugar is expelled through urine, which gives rise to the term ‘diabetes’.
Diabetes can be divided into 2 types :
Type 1 diabetes is caused by the inability of the pancreas to produce the hormone insulin. This is mostly found in children.
Type 2 diabetes is caused by the pancreas not producing enough of the insulin hormone, or by a condition called Insulin Resistance, mostly found in adult and elderly.
Symptoms of diabetes :
- Thirsty
- Dry mouth
- Frequent urination
- Frequent hunger, unusual weight loss or gain
- Feeling tired easily
- Numbness, especially in the hands and legs
- Wounds are hard to heal

Complications of diabetes :
- Complications of clogged arteries often occurring in the legs. It is common to have pain in the legs. Untreated it may cause blood clots until the toes lack blood. Narrowing of blood vessels.
- Coronary arteries: The blood supply to the heart is blocked causing the heart to lack blood. May cause myocardial infarction.
- Cerebrovascular disease: resulting in paresis, paralysis, crooked mouth, slurred speech, or half numbness.
- Eye complications such as amblyopia, diabetic retinopathy, and retinopathy.
- Kidney complications causing renal failure.
- Neurological complications such as numbness in the feet and hands, and possibly pain.
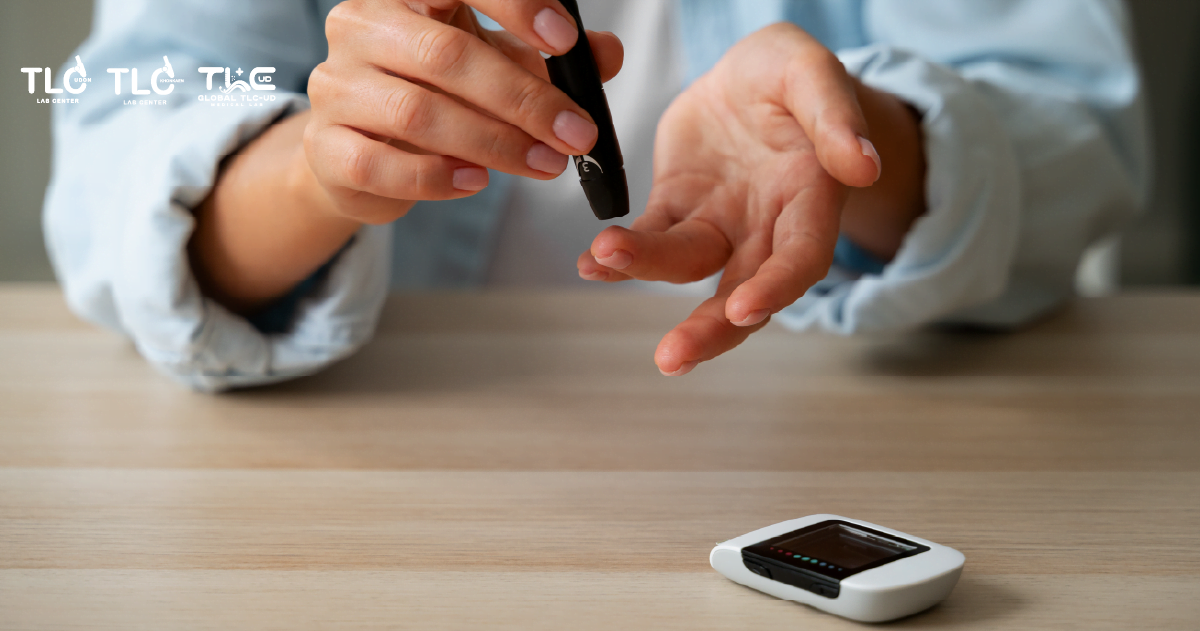
Who should be tested for diabetes?
- People who are overweight and have body mass index (BMI) ≥ 25 kg/m2
- People with a family history of diabetes.
- High blood pressure (greater than 140/90 mm Hg) and HDL-cholesterol level ≤ 35 mg/dl and/or triglycerides ≥ 250 mg/dl in the blood.
- Women with gestational diabetes.
- People without symptoms but older than 35 years. (In case of normal blood testing result, repeat check-up every 3 years)
Prevention of diabetes :
- Consume nutritious foods that contained high in fiber.
- Reduce the consumption of sugary foods and sweetened beverages.
- Avoid drinking alcohol and smoking.
- Exercise regularly.