What is dengue fever?
Dengue haemorrhagic fever : It is a disease caused by infection with the dengue virus carried by Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. After the fever subsides, there may be bleeding in various organs, or shock which is dangerous as patients often think that after the fever subsides, it is safe. It is important to notice any abnormal symptoms after the fever has subsided for 2-3 days and then rush to the hospital for treatment if found.It usually found in tropical countries and It spreads during the rainy season every year.
Causes of dengue fever
There are 4 strains of dengue virus:
- Strain DENV-1
- Strain DENV-2
- Strain DENV-3
- Strain DENV-4
There are female Aedes mosquitoes that carry diseases. When Aedes mosquitoes suck the blood of patients with the dengue virus, the infection enters the mosquito’s stomach and salivary glands with an incubation period of 8-12 days.
When mosquitoes carrying the virus go on to bite other people, the virus enters the bloodstream of the bitten person, causing the spread of dengue haemorrhagic fever as follow
Dengue patients who have been exposed to a particular strain of the virus have immunity to that particular strain. If they are infected with a different strain of the virus, they can get dengue fever again, and the symptoms of the second disease are generally more severe than the first.
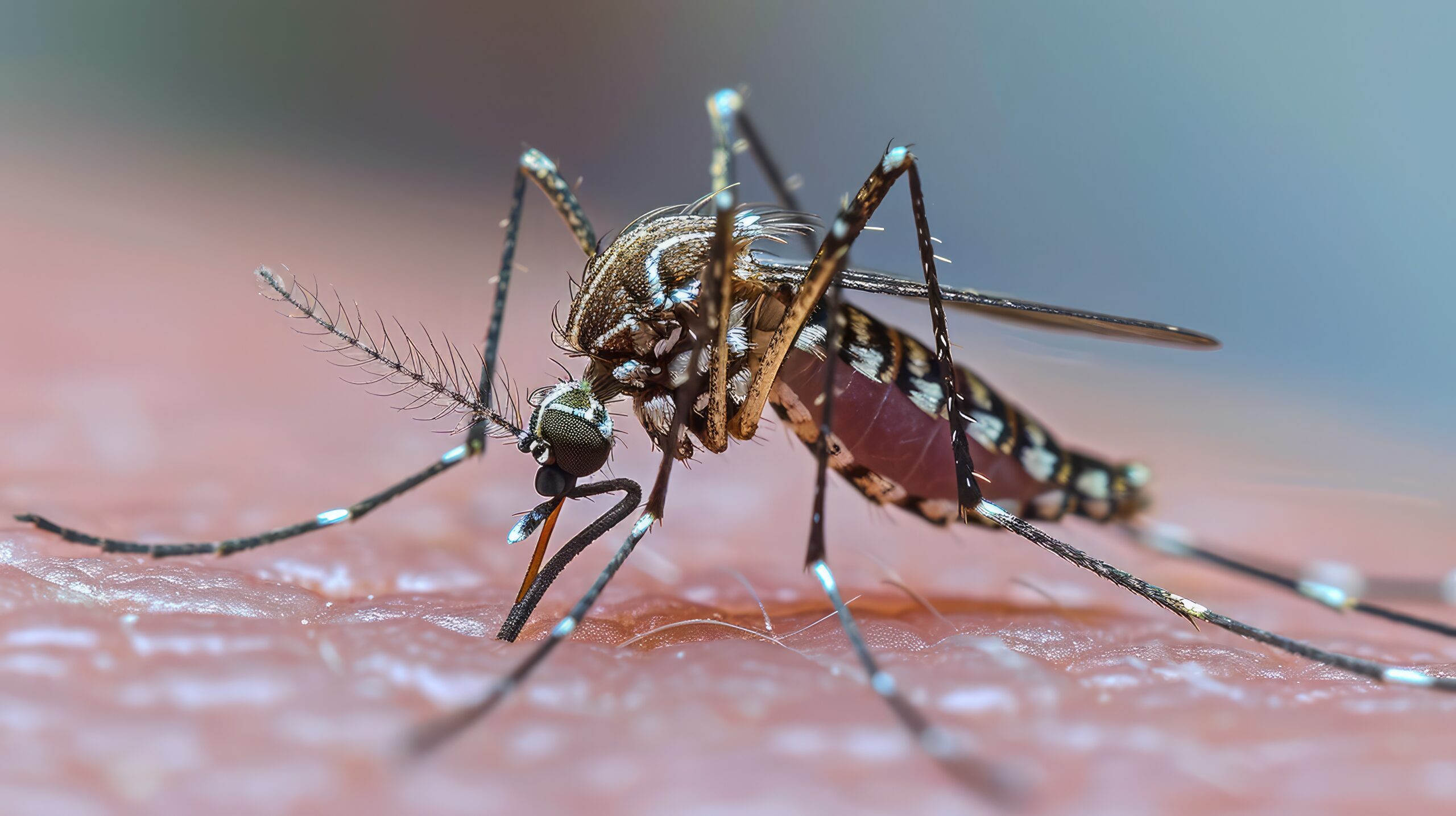

Risk factors for dengue fever
Dengue fever can be found at any age. However, it is more common in school-age and early working age children, where patients at risk of severe disease progression or complications include:
- Infants and the elderly
- Pregnant women
- People with stomach ulcers
- Women who are on their period or have abnormal vaginal bleeding.
- People with haemolysis or haemoglobin disorders
- Patients with congenital heart disease
- Patients with chronic diseases such as diabetes and blood pressure, ischemic heart disease, kidney failure, and cirrhosis of the liver.
- People taking corticosteroids or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Symptoms of Dengue Virus
They are divided into 2 types according to severity:
- Dengue Fever
- Dengue haemorrhagic fever
Symptoms of Dengue Fever
- Headache
- Pain in the eyes
- Body aches
- Joint or bone pain
- A rash resembling measles.
- Bleeding may or may not be present.
Symptoms of dengue haemorrhagic fever:
In addition to having the same symptoms as dengue fever, there are other symptoms which are characteristic of the disease:
- Acute high fever exceeding 38 degrees Celsius for 2-7 days
- Nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite.
- Red face: Small red blotches or bleeding spots may appear on the skin, or bleeding in other areas such as nosebleeds. Scurvy, bloody stools.
- Severe abdominal pain; Tenderness on the right side of the ribcage
- In very severe cases, after several days of fever, the patient may develop circulatory failure or anaphylactic shock and enter a stage called dengue shock syndrome,The patient show symptoms involving the restless, cold hands and feet ,urinating less, low blood pressure, can’t measure pulse.
Dengue Fever Treatment
Currently, there are no antiviral drugs for dengue fever. Therefore, treatment is based on symptoms to support the patient’s body to return to normal as soon as possible. Dengue fever may resolve on its own within 2-7 days.
Primary symptom care
- Wipe away sweat to reduce the fever and give antipyretic medication as prescribed by the doctor, including paracetamol, every 4-6 hours, if the fever lasts more than 3 days, you should see a doctor.
- Do not give antipyretic drugs containing aspirin or ibuprofen as they can cause gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Drink plenty of liquids, and fruit juice or salt water are recommended instead of water.
- Avoid spicy foods of any kind, as they may irritate the stomach.
- Avoid foods that are red or black, as this can be confused with gastrointestinal bleeding.
See a doctor immediately. If you have any of the following symptoms:
- Excessive vomiting. Inability to eat enough food and water.
- Severe abdominal pain.
- Severe bleeding such as black bowel movements and vomiting blood.
- Restlessness, sweating, cold body, cold hands and feet.
- Unable to urinate for more than 6 hours.
Dengue prevention
Dengue fever can be prevented as follows:
- Prevent Aedes mosquito bites by wearing fully covered clothing. Use repellents such as DEET and prevent Aedes mosquitoes from hiding in the house. Aedes mosquitoes often bite during the day rather than at night.
- Destroy breeding sites for Aedes mosquitoes around your home and nearby. Closing the lids of containers of standing water to prevent mosquitoes from entering to lay eggs. Change the water in any containers that cannot be closed, such as a vase, every week. Improve the environment around the house to be clean and free from debris that may be waterlogged, such as old bottles, old cans, etc.
- Patients over 9 years old and less than 45 years old with a history of dengue fever may consider vaccination against dengue fever.
Laboratory diagnostics
- Complete blood count (CBC) : To look for abnormalities in all components of blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and blood concentration.
- Immune test against dengue fever (IgM)
- NS1 Ag test directly to the infection, PCR test for dengue virus












