Understanding the Ketogenic Diet
The Ketogenic Diet, commonly known as the “Keto Diet”, focuses on high fat and moderate protein intake, while significantly reducing carbohydrates.Carbohydrates must be reduced as much as possible or very little in each meal with the aim of causing the body to the process of breakdown fat until creating a substance called ketone that help with metabolism very well.Therefore it is considered as an interesting way to control.weight from eating.Including suitable for diabetics who want to control their blood sugar as well.
Principles of the Ketogenic Diet
The core principle of the Keto Diet is to minimize carbohydrate intake from foods like starches, rice, potatoes, sugars, juices, and certain fruits. These carbohydrates, when consumed, are converted into glucose, causing a spike in blood sugar and insulin levels. By reducing carbohydrate intake, the body’s glucose levels drop, and insulin levels decrease accordingly. As a result, the body starts utilizing fat for energy, leading to a state of ketosis.
Who Can Benefit from the Keto Diet?
- People with Diabetes: The Keto Diet can help in managing blood sugar levels.
- Individuals Looking to Lose Weight: The diet can be effective for weight loss by promoting metabolism.
Who Should Avoid the Keto Diet?
- People with Liver Disease
- Patients with Kidney Disease
- People who have problems with metabolism or who have high cholesterol or triglycerides
- People with Gastrointestinal Issues: Those prone to bloating, acid reflux, or poor intestinal motility may find that the diet exacerbates their symptoms.
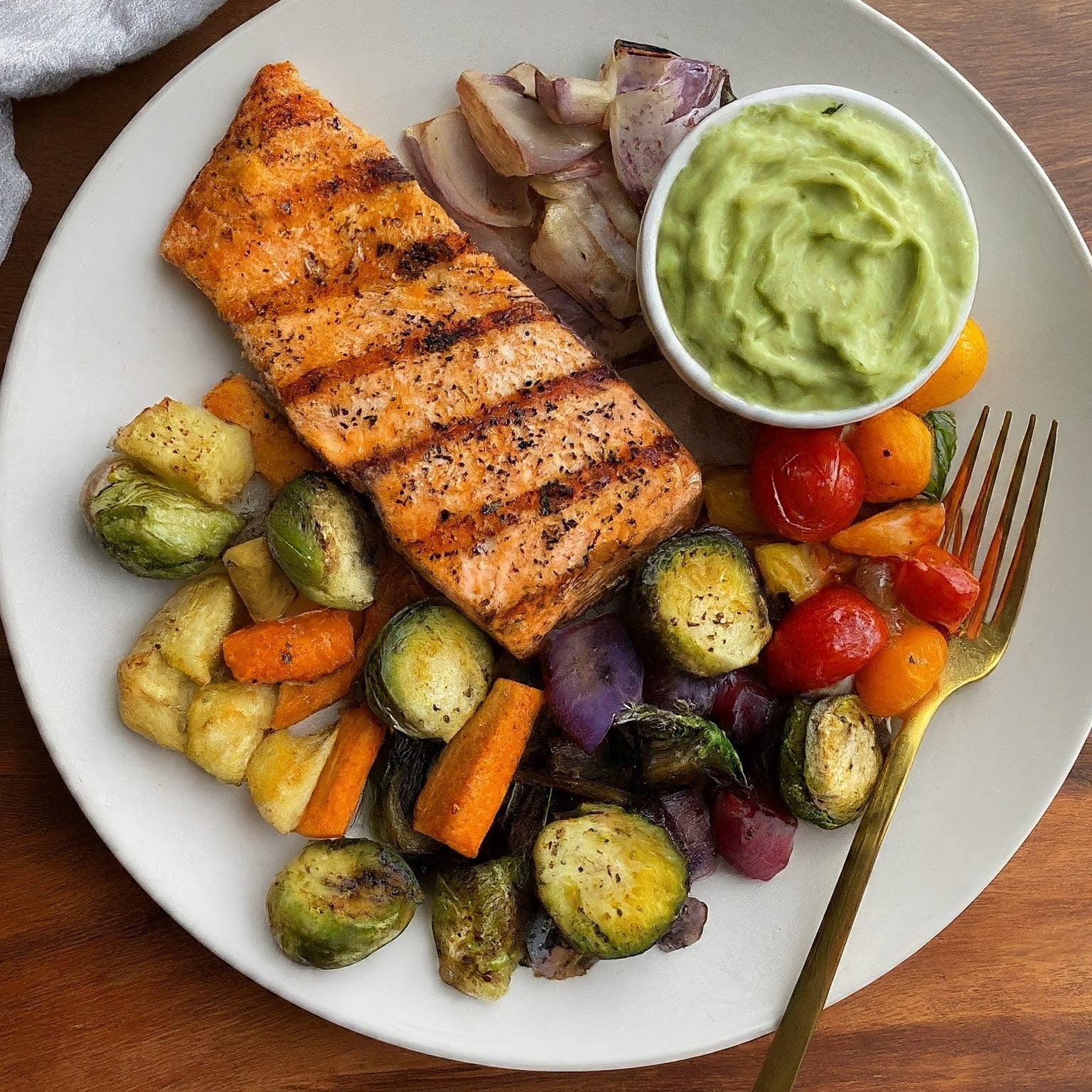
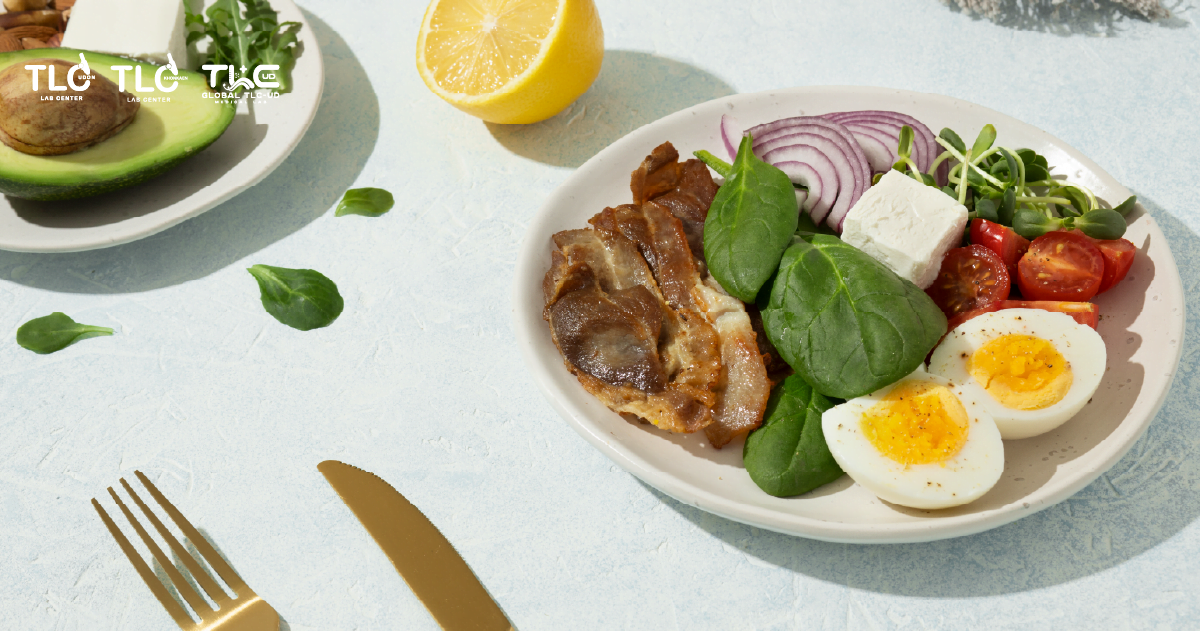
A balanced and healthy Keto Diet should focus on fresh, unprocessed foods. The diet is categorized into three main groups:
- Fat
- Protein
- Low-Carbs
Fatty Foods
Prioritize natural and healthy fats, including monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA) and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs):
- Nuts: Pistachios, almonds, walnuts, etc.
- Oils: Olive oil, sunflower oil, soybean oil, canola oil, rice bran oil, corn oil.
- Other Sources: Avocado, butter, cheese, and sea fish.
Protein-rich Foods
Include both animal and plant-based proteins:
- Meat: Pork, chicken, fish.
- Animal Products: eggs, milk.
- Plant-based Proteins: Soybeans, tofu, chickpeas, pumpkin seeds.
Low-Carb Foods
Incorporate foods with low carbohydrate content:
- Meat and Eggs: Chicken, pork, beef, chicken eggs, duck eggs.
- Dairy Products: Mozzarella cheese, blue cheese.
- Beverages: Coffee, tea, dark chocolate, and cocoa (without sugar).
- Vegetables: Leafy greens, broccoli, mushrooms, spinach, cauliflower, bell peppers, etc.
- Fruits: Dragon fruit, green apples, berries, guava, oranges.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can follow the Keto Diet in a safe and healthy manner, ensuring you get the necessary nutrients while promoting effective metabolism and overall well-being.
Benefits of the Keto Diet
Key Benefits
- Helps with Weight Loss
The ketogenic diet prompts the body to burn fat for energy, a state known as “ketosis,” leading to effective weight loss. - Improved Metabolism
Reducing carbohydrate intake stabilizes blood sugar and insulin levels, positively affecting the metabolic system. - Brain Health
Good for the brain: It is used to treat diseases related to brain disorders such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, and can also reduce the frequency and severity of seizures in children with epilepsy. - Lowers Blood Sugar Levels
The diet naturally lowers blood sugar levels by minimizing carbohydrate intake. - Lowers Insulin Levels
By reducing carbs, the diet decreases the need for insulin, helping to lower insulin levels in the body.
Pre-Diet Health Checks
Before starting the Keto Diet, it’s essential to assess your overall health through various blood tests to ensure it’s suitable for you. Recommended tests includes:
- Blood Sugar and Accumulated Sugar Levels
Tests: Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS), Haemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), Insulin Level. - Liver Function
Tests: Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST), Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT). - Kidney Function
Tests: Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN), Creatinine, Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR). - Lipid Profile
A comprehensive lipid profile to monitor cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
Regular monitoring and consultation with a healthcare professional are crucial to follow the Keto Diet safely and to reap its benefits effectively.