In the world of wellness, especially when it comes to anti-aging and cellular rejuvenation, one compound has been steadily gaining attention: NAD+. Many longevity-focused approaches aim to maintain or boost NAD+ levels through various means—such as targeted supplements, intermittent fasting, nutrient-dense diets (rich in vitamins A, B-complex, C, E, and zinc), regular physical activity, stress management techniques, and mindfulness practices.
NAD and NADH: An Overview
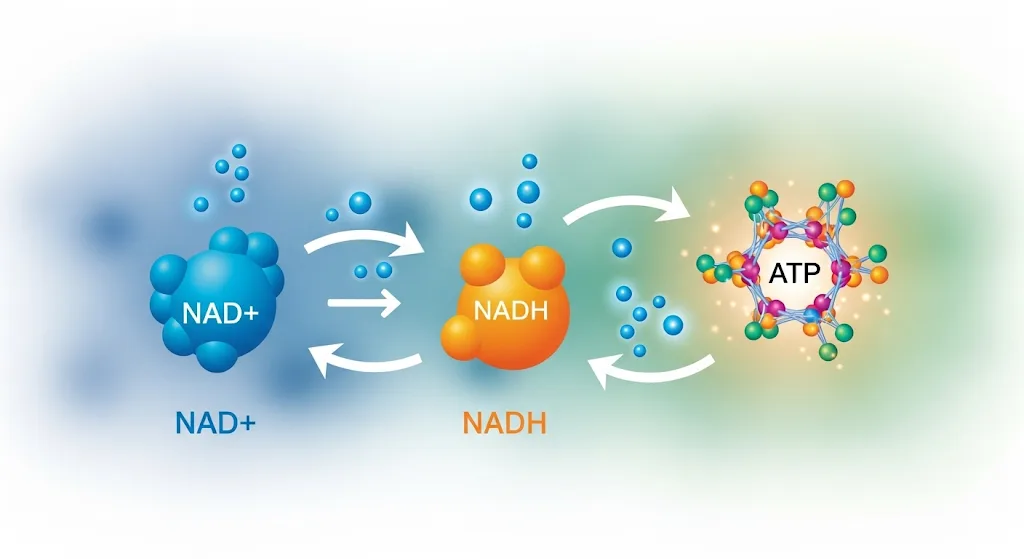
NAD stands for Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide—a critical molecule found in every living cell. It acts as a coenzyme, supporting countless metabolic functions—most notably those involved in energy production.
NAD exists in two interconvertible forms:
- NAD+ (the oxidized form)
- NADH (the reduced form, after accepting electrons or hydrogen)
Think of them like a power circuit: NAD+ captures electrons and becomes NADH. Later, NADH donates those electrons, converting back into NAD+ to continue the cycle.
How Do NAD and NADH Support the Body?
- Energy Metabolism (Cellular Respiration):
NAD+ is essential for converting food—carbohydrates, fats, and proteins—into usable cellular energy, or ATP. During glycolysis and the Krebs cycle, NAD+ collects electrons and becomes NADH. This NADH then carries the electrons into the mitochondria, where they’re used to generate ATP. Without this system, the body would be unable to extract energy from food efficiently. - DNA Maintenance and Cell Longevity:
NAD+ fuels key enzymes—such as PARP and sirtuins—that repair DNA, regulate inflammation, and delay cell aging. Maintaining healthy NAD+ levels may help protect cells from age-related deterioration. - Antioxidant Defense:
NADH helps facilitate the production of antioxidant compounds that shield cells from oxidative damage. - Broader Functions: Beyond energy and repair, NAD/NADH are involved in cell signaling, gene regulation, and immune response.
Why NAD/NADH Matter for Your Health
- Boosts Energy Reserves : Plays a foundational role in metabolism, stamina, and combating fatigue.
- Supports Healthy Aging : Key for DNA repair, cellular health, and promoting a longer, healthier life. (NAD+ levels naturally decline as we age.)
- Enhances Brain Function : Crucial for maintaining cognitive clarity, focus, and nerve cell activity.
- Cellular Protection : Helps defend the body against toxins, inflammation, and everyday stressors.
- Potential in Therapeutics : Ongoing research is exploring NAD/NADH supplementation as a promising approach for managing chronic fatigue, neurodegenerative conditions, and other age-related issues.
Laboratory Assessment
To evaluate cellular health and aging, specialized blood tests may include:
- NAD+
- NADH+
- Telomere range
References
- Verdin, E. (2015). NAD+ in aging, metabolism, and neurodegeneration. Science, 350(6265), 1208–1213. [ science.org ]
- Ying, W. (2008). NAD+/NADH and NADP+/NADPH in cellular functions and cell death: Regulation and biological consequences. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 10(2), 179–206. [ liebertpub.com ]
- Imai, S., & Guarente, L. (2014). NAD+ and sirtuins in aging and disease. Trends in Cell Biology, 24(8), 464–471. [ cell.com ]
- Bogan, K. L., & Brenner, C. (2008). Nicotinic acid, nicotinamide, and nicotinamide riboside: A molecular evaluation of NAD+ precursor vitamins in human nutrition.Annual Review of Nutrition, 28, 115–130. [ annualreviews.org ]