Cellular regeneration refers to the body’s natural ability to repair or replace damaged cells with new ones. This process is essential for maintaining balance within the body and for healing damage caused by aging, injuries, or environmental stressors such as pollution, UV radiation, and toxins.
Types of Cellular Regeneration
Cell regeneration can be broadly categorized into two main types:
- Physiological Regeneration
This occurs regularly as part of normal bodily function. Examples include:- Skin cells renewing every 28 days
- Intestinal lining cells regenerating every 3–5 days
- Red blood cells cycling every 120 days
- Repair Regeneration
This refers to the body’s response to injury, where damaged tissue is restored. Examples include:- Wound healing
- Liver regeneration after partial removal
- Muscle recovery following intense exercise
Key Mechanisms Involved in Cellular Regeneration
- Stem Cells: These are undifferentiated cells capable of developing into various cell types as needed.
- Autophagy: A cellular “clean-up” process that removes damaged components and recycles them for reuse.
- Mitochondria: Often called the powerhouse of the cell, mitochondria play a critical role in both energy production and repair when cells are damaged.
- Antioxidants: These substances help reduce oxidative stress, a major factor in cellular damage.
Factors That Support Cellular Regeneration
- Adequate sleep
- Intermittent fasting
- Regular physical activity
- A nutrient-rich diet, particularly high in vitamins A, C, E, B-complex, and zinc
- Stress reduction and mindfulness practices
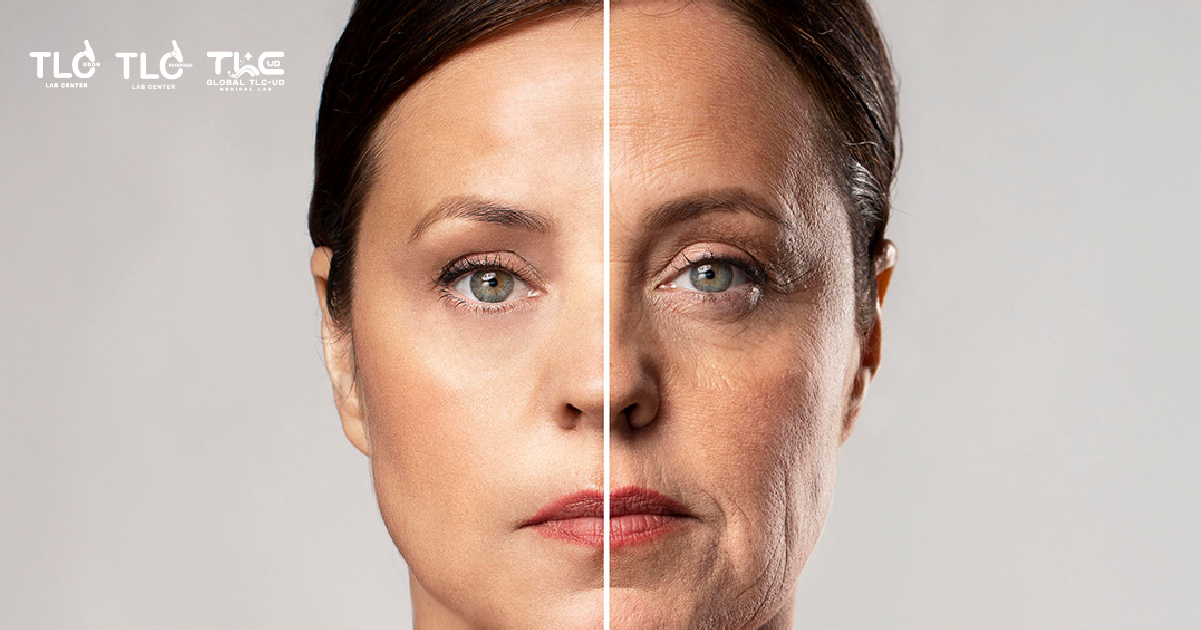
Cellular Regeneration and Its Role in Anti-Aging and Disease Prevention
Cellular Regeneration and Aging
As we age, the body’s ability to regenerate cells slows down. Some cells stop dividing altogether (cellular senescence) or accumulate damage, which can lead to visible signs of aging, such as:
- Wrinkled skin
- Muscle weakness
- A weakened immune system
- Greater susceptibility to chronic diseases like diabetes, cancer, and heart disease
- Supporting ongoing cell renewal is a key strategy in slowing the aging process at the cellular level, promoting long-term health and resilience.
Cellular Regeneration and Disease Prevention
Cellular Regeneration and Disease Prevention
Cell degeneration is linked to many chronic conditions:
- Chronic Diseases:
- Type 2 Diabetes : Damage to insulin-producing pancreatic cells
- Cardiovascular Disease : Resulting from degeneration of blood vessel linings
- Cancer : Mutated cells not effectively removed from the body
- Neurodegenerative Diseases:
Conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s are associated with the brain’s declining ability to regenerate neurons.
Modern Technologies and Therapies That Support Cell Regeneration
- Stem Cell Therapy: Uses stem cells to repair or replace damaged tissues.
- Exosome Therapy: Delivers intercellular signalling molecules to promote healing and reduce inflammation.
- NAD+ Boosters (e.g., NMN or NR): Enhance cellular energy and improve DNA repair mechanisms.
- Autophagy Fasting: Fasting methods that trigger cellular cleansing processes.
- Senolytics: Compounds designed to eliminate aging or “senescent” cells that can negatively affect tissue health.
Nutrients That Promote Cellular Regeneration
| Nutrient | Sources | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C, E | Fruits, vegetables, nuts | Boost collagen production, aid skin repair |
| Coenzyme Q10 | Fish, meat, avocados | Enhances mitochondrial energy production |
| Resveratrol | Red grapes, berries | Activates longevity genes (Sirtuins) |
| Sulforaphane | Broccoli | Supports cellular detox pathways |
| Omega-3 fatty acids | Fatty fish, flaxseeds | Reduces inflammation, supports tissue repair |
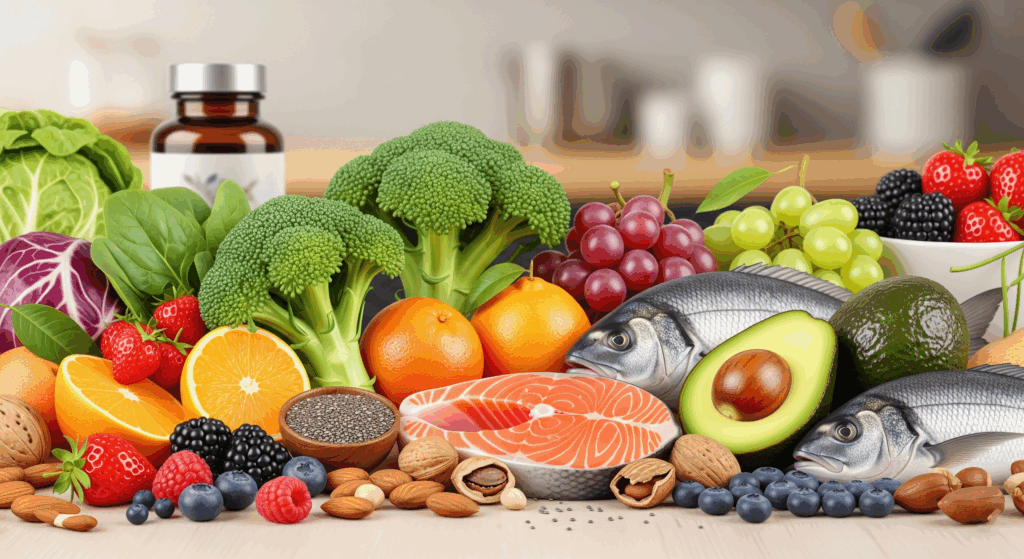

Lifestyle Habits That Encourage Cellular Regeneration
- Sleep 7–9 hours per night: Deep sleep (especially between 10:00 PM and 1:30 AM) is when most cell repair occurs.
- Exercise regularly: Especially high-intensity interval training (HIIT) and resistance training.
- Limit sugar and processed foods: Reduces chronic inflammation that can impair cellular function.
- Practice mindfulness or deep breathing: Helps lower stress hormones that negatively affect cell health.