Can cancer be found in all genders and ages?
Cancer can affect people of all genders and ages, from the time of birth to old age. It’s most frequently diagnosed in individuals aged 50 and above. However, the occurrence is significantly lower in children, approximately one-tenth as common as in adults.
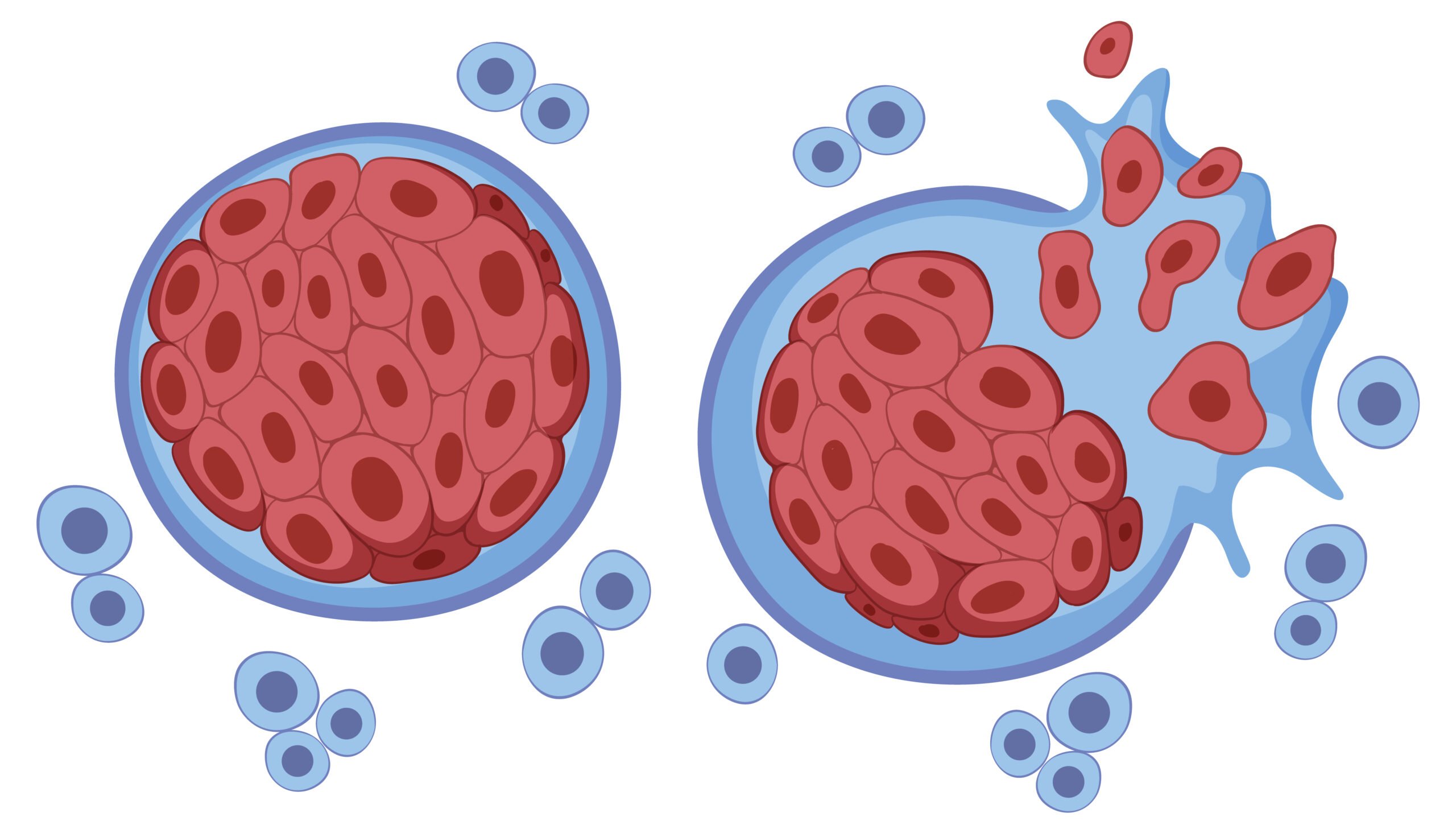
Tumour classification could be classified into 2 types :
- Malignant tumour
Malignant tumour or cancer is a disease caused by the presence of abnormal cells in the body, which uncontrollable growing and which the body can’t control. These cancer cells multiply and spread throughout the body through the blood stream, lymph nodes or lymphatic system and body cavity. Once metastasized, these cancer cells implant and multiply in the destination organ. As a result, the normal cells of various tissues and organ fail and are unable to function normally. It causes eventual death involving lungs, liver, brain, kidneys, bones, and bone marrow
2. Benign tumour
Benign tumours are lumps and bumps that grow abnormally. They are caused by cells or tissues in the body growing and multiplying rapidly, but this type of tumour will not spread to other tissues or organs.
Commonly occurring cancer
Common cancers in men include:
- Liver cancer
- Lung cancer
- Colon cancer
- Prostate cancer
- Lymphoma
- Leukaemia
- Bladder cancer
- Oral cancer
- Stomach cancer
- Oesophageal cancer
Common cancers in women are:
- Breast cancer
- Cervical cancer
- Liver cancer
- Lung cancer
- Colon cancer
- Ovarian cancer
- Leukaemia
- Oral cancer
- Thyroid cancer
- Lymphoma
Common cancers in children are:
- Leukaemia
- Lymphoma
- Brain tumour and brain cancer
- Neuroblastoma/ Neuroblastoma (Cancer of the sympathetic nervous system)

Causes and risk factors that cause cancer.
Currently, we are not able to identified the exact cause of cancer whether it is from a single cause or from a variety of causes. Hence, awareness of them and awareness of the factors that may cause cancer can help reduce the risk of this disease.
Causes and risk factors that may cause cancer can be classified as follows:
External factors
- Exposure to radiation and chemicals in the environment ️
- Exposure to radiation and radioactive substances such as uranium or ultraviolet (UV) rays in sunlight can increase your risk of skin cancer.
- Having a previous history of radiation therapy for cancer may increase the risk of recurrence of cancer such as lung cancer, breast cancer, thyroid cancer.
- Cigarettes and inhalation of cigarette smoke. It is the main risk factor for cancer and can cause serious health problems. People who regularly smoke or inhale tobacco smoke are more likely to develop cancers such as lung cancer, mouth and throat cancer, laryngeal cancer, oesophageal cancer or cervical cancer.
- Alcohol. Drinking alcohol is a risk factor for liver cancer, stomach cancer, and colon cancer.
- Exposure to carcinogenic substances such as benzene, asbestos, cadmium, nickel, polyvinyl chloride, pesticides, radon, uranium. diesel exhaust or products from coal
- Food carcinogens, such as char-grilled, grilled or fried foods. Aflatoxin, a toxin caused by fungi hydrocarbons such as nitrosamines that are present in fermented foods.
- Taking too much oestrogen. A relationship found with breast cancer and endometrial cancer from receiving too much oestrogen
- Various infectious diseases
- Viral infections such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), HPV virus, Hepatitis B & C virus.
- Bacterial infections such as Helicobacter pylori bacteria increase the risk of gastric cancer. Salmonella Typhi increases the risk of gallbladder cancer, for example.
- Infection with certain parasites, such as Opisthorchis viverrini, from eating freshwater fish or undercooked food contaminated with worm eggs, which is the main cause of bile duct cancer
Internal factors
- Having a family history of cancer. This type of cancer is caused by a genetic abnormality, or some genetic material.
- Aging : Advancing age may increase your risk of developing cancer.

Signs and symptoms of cancer:
Many cancers have no symptoms in their early stages, and some cancers are in organs that are difficult to detect. May be obscured by other organs in the body until cancer cells have spread to the other organs when the signs and symptoms of cancer will be more clearly displayed. The signs and symptoms of cancer that should be seen by a doctor for diagnosis include :
- Abnormal bleeding in areas such as the anus, cervix
- Dysphagia. Often feel heartburn
- Chronic fever
- Blood in the urine and difficulty urinating
- The stool is black or has blood in it, having difficulty passing stools.
- Chronic cough, cough with blood-tinged sputum, and hoarse voice.
- Body aches, bone pain.
- Wounds heal slowly or are chronic in their nature.
- You can feel a lump on your neck, breast, or any other part of your body.
- A mole, wart, or birthmark on your body enlarges, itches, or bleeds.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Fatigue, loss of appetite.
- Abnormal vaginal discharge, vaginal bleeding.

Stages of cancer.
Cancer stage is a measure of the severity of the disease by its spread. tells treatment guidelines. And doctors use it in research studies related to cancer.
Generally, cancer has 4 stages :
- Stage 1: The cancer is confined to a small area and has not spread.
- Stage 2: The cancer has grown within the organs but has not spread to the lymph nodes. or other tissue
- Stage 3: The cancer has grown in size. and may spread to lymph nodes or other tissue
- Stage 4: The cancer has spread to other organs. or other parts of a distant body.
How to treat cancer
Cancer treatment can be done in a number of ways. depending on the location, type, stage of the disease and individual needs as follows :
- Surgery: Surgery is the main option for patients with cancer in the early stages. It can be completely cured. In some cases, it may be combined with radiation therapy or chemotherapy to shrink cancer cells before surgery.
- Radiation therapy (Radiotherapy) uses high intensity radiation to shrink tumours through killing cancer cells. This method is often used in combination with chemotherapy during surgery. Radiation therapy may be the main treatment option for patients with advanced cancer.
- The use of chemotherapy drugs (Chemotherapy). Giving drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells through orally consuming them or injecting them into a blood vessel. Chemotherapy can also be used to relieve pain from cancer tumours.
- Targeted therapy: Targeted therapy focuses on killing cancer cells. By stopping the growth of abnormal cells without affecting normal cells. The doctor will examine the gene mutation first.
- Immunotherapy relies on the principle of using the immune system to deal with cancer cells in the body through injections to interrupt the production of proteins that cancer cells use to prevent the immune system from attacking them.
Integrated care and pain management (Palliative care and pain management) is a form of palliative care provided to patients. Research has found that by having strong mental health after being diagnosed with cancer and undergoing treatment, patients can live up to 3 months longer if they receive good support from those around them.
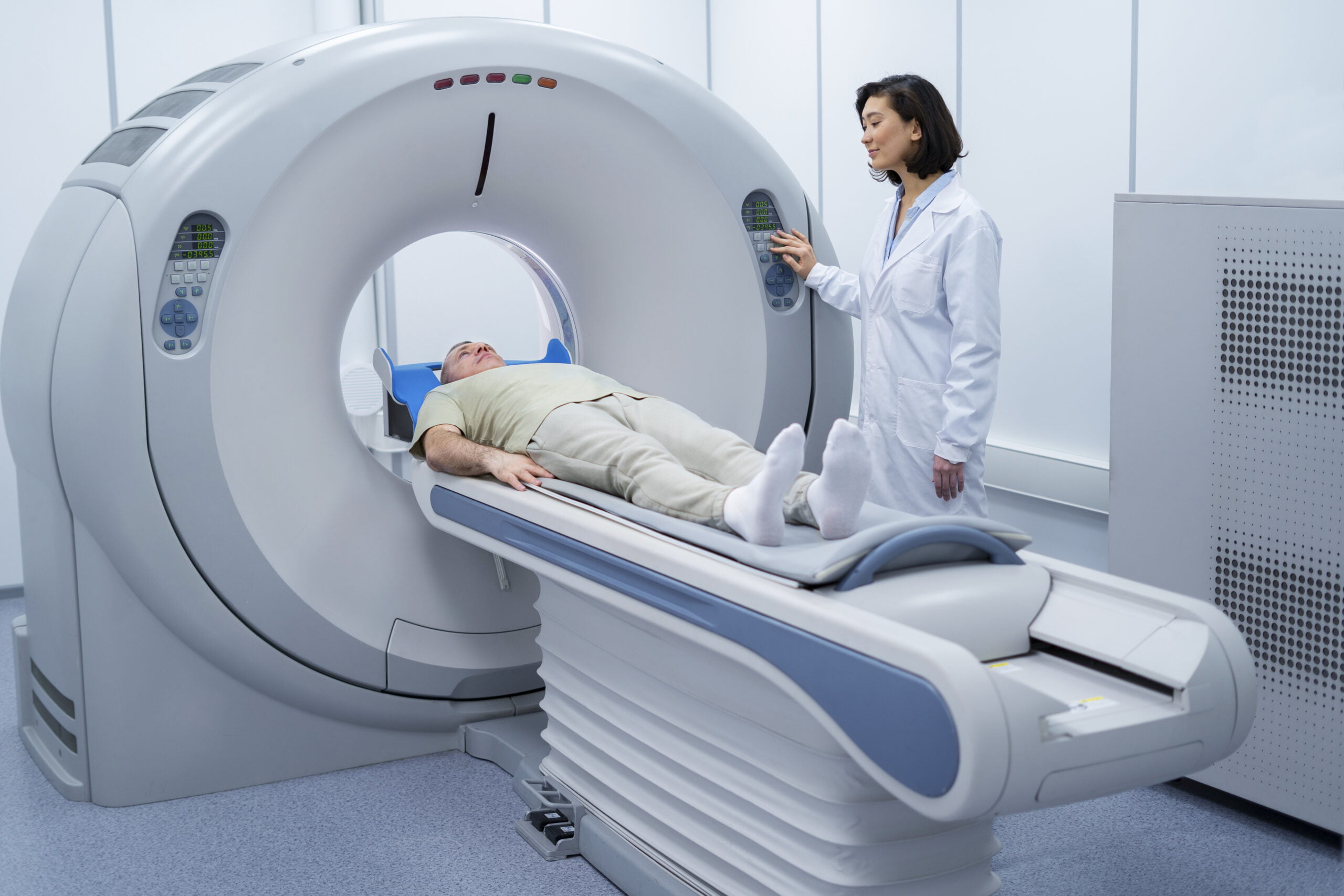
Cancer screening and diagnosis
- From a tissue examination (Pathology diagnosis by a pathologist.)
- X-ray examination or CT scan (Computed tomography) that will show the location of cell abnormalities in the body more accurately than general x-rays.
In some cases, doctors can detect cancer cells from secretions such as sputum (Sputum cytology), fluid in the abdomen (Ascites fluid cytology), fluid in the pleural fluid (Pleural fluid cytology), which can sometimes tell the origin and types of cancer cells
Gene testing because of the risk of cancer from genetics. Initial screening and risk assessment can be performed by genetic testing, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, which are associated with breast cancer and ovarian cancer, etc.
Currently, basic cancer screening is done by drawing blood. Laboratories look for cancer markers (Tumour makers) such as PSA (prostate cancer), AFP (liver cancer), CEA (colon cancer), CA153 (breast cancer), CA125 (ovarian cancer), CA199 (cancer Pancreas and bile duct), NSE(Neuron Specific Enolase(Lung cancer)although it is still a method that cannot replace biopsy for diagnosis. But the method of detecting cancer markers in combination with other cancer detection methods will help to make the diagnosis with high accuracy. It also checks the risk and chance of cancer and that is useful in taking good care of your health in a preventative way.
Cancer screening
Cancer screening is the process of detecting cancer before it has symptoms. (Often cancer is stage 0 or stage 1) This is because cancer at this stage has a higher chance of being cured than cancer at other stages. Effective cancer screening is a test that, when the disease is found, after treatment, patients will have a higher cancer survival rate or a lower cancer death rate.
Currently, effective cancer screening is for cervical cancer, breast cancer, and colon cancer.
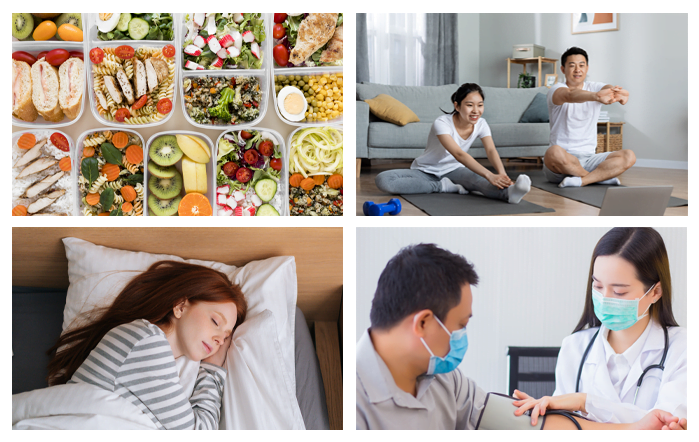
Cancer prevention :
The best way to prevent cancer is to avoid important risk factors :
- Eat nutritious food every day in the right amount, that is, neither too fat nor too lean, by limiting red meat, starch, sugar, fat, salt, but adding lots of vegetables and fruits.
- Exercise appropriately and regularly.
- Get enough sleep.
- Relax and stress relief.
- Avoid carcinogenic substances.
- Go for cancer screening/annual health check. If interested in getting checked, click here.

Reference:
- Dr. Supreeda Chainithikarn (Physician, Expert in medical oncology)
- Thai Health Promotion Foundation. (2017, August 9). Cancer’s Risk factor. Retrieved from [thaihealth.or.th]
- Institute National Cancer. (n.d.). Basic knowledge of cancer. Retrieved from [nci.go.th]