Fatty liver disease can affect anyone, not just those who are obese. This condition is often caused by lifestyle habits such as drinking alcohol, consuming a diet high in unhealthy fats, neglecting fruits and vegetables, and, most importantly, not exercising. Modern life, with its constant hustle and limited time, leads many people to consume more processed and fast foods, unaware of the silent dangers these choices pose to their health.
People in high-risk groups, including those who are obese, who have a belly, are overweight, or suffer from diabetes, hyperlipidaemia, and hypertension, are 60% more likely to develop fatty liver disease compared to the general population. Unfortunately, this disease often presents few or no symptoms, making it a hidden health risk.

What is Fatty Liver Disease?
Fatty liver disease is a condition where fat, especially triglycerides, accumulates in the liver. If the fat makes up more than 5-10% of the liver’s weight, it is considered fatty liver disease. This condition can lead to hepatitis or fibrosis within the liver and can rapidly progress to cirrhosis and, eventually, liver cancer.
Phases of Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease can be divided into four stages:
- Stage 1: Fat accumulation in the liver.
- Stage 2: Inflammation of the liver, leading to liver cell damage and abnormal liver function. If this stage lasts for more than six months, it can result in chronic hepatitis.
- Stage 3: Fibrosis within the liver and its blood vessels. If the underlying cause is treated, the progression of the disease can be halted.
- Stage 4: Cirrhosis, where the liver is permanently damaged and fibrous tissue spreads throughout the liver, leading to liver failure and potentially liver cancer.
Causes of fatty liver disease
Fatty liver disease is caused by 2 factors:
- Alcohol fatty liver disease is caused by drinking excessive amounts of alcohol.
- Non-alcohol related fatty liver disease (NAFLD) occurs in non-alcoholic people such as obesity (high triglycerides), type 2 diabetes, hyperlipidaemia, and high blood pressure.
Risk factors for fatty liver disease
1. Metabolic syndrome, which consists of:
- Waist circumference that exceeds 90 cm in women.
- Waist circumference exceeding 100 cm in men.
- high blood pressure
- High triglyceride levels greater than or equal to 150 milligrams per decilitre.
- HDL levels are less than 40 mg/dL in males and less than 50 mg/dL in females.
- High blood sugar of more than 110 milligrams per decilitre.
2. Diabetes, obesity, and hyperlipidaemia.
3. Regular high-energy foods such as fat, sugar, starch.
4. Menopause: some post-menopausal women are at higher risk.
5. Side effects from certain drugs such as some chemotherapy drugs, steroid drugs. Certain antiviral drugs can contribute to fatty liver disease.

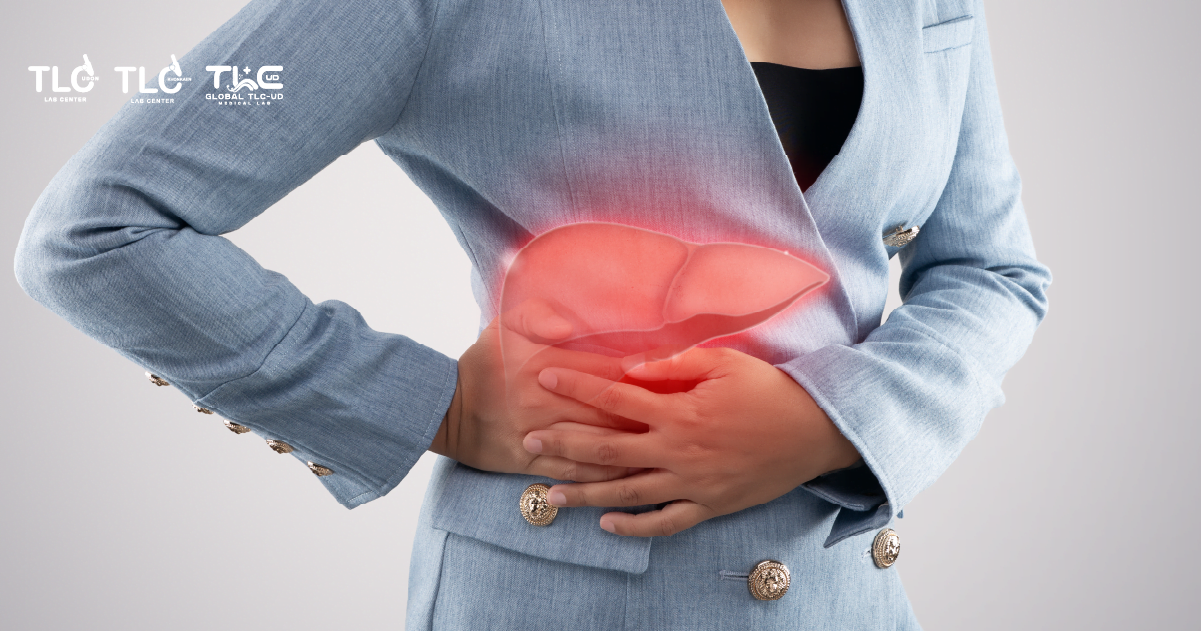
Warning Signs of Liver Disease:
- Fatigue and exhaustion
- Yellow skin and yellow eyes
- Dark urine
- Bloating and a feeling of gas in the stomach
- Nausea and vomiting
- Pain under the right rib cage
Preventing Cirrhosis and Fatty Liver
- Stop smoking: Avoid smoking and exposure to second-hand smoke.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Avoid drinking alcoholic beverages.
- Eat Healthy Foods: Avoid high-fat foods such as milk, butter, cheese, coconut milk, and certain seafood.
- Choose Healthy Fats: Focus on consuming fats with high nutritional value, such as those found in olive oil, avocados, and omega-3 fish oil.
- Increase Fruit and Vegetable Intake: Incorporate more fresh fruits and vegetables into your diet.
- Exercise Regularly: Aim for at least 160 minutes of exercise per week.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Ensure your body weight stays within a healthy range.
- Regular Bowel Movements: Avoid constipation to maintain digestive health.
- Consult Your Doctor About Medications: If you take medications regularly, consult with your doctor to ensure they do not harm your liver.
- Manage Existing Conditions: Effectively treat conditions like diabetes, hyperlipidaemia, and obesity to keep them under control.
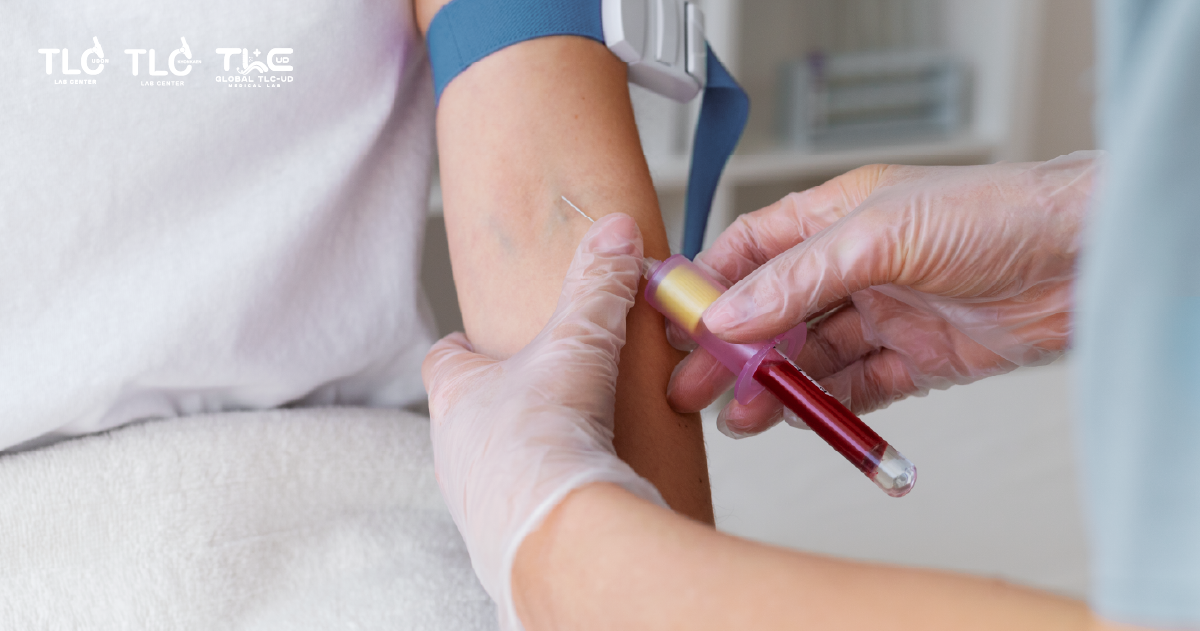
Diagnosis of Fatty Liver Disease in the Laboratory
1.Lipid Profile:
- Total cholesterol , HDL, LDL, Triglycerides
2. Liver Function Tests:
- AST(Aspartate Aminotransferase)
- ALT(Alanine Aminotransferase)
3. AFP (Alpha-Fetoprotein) Liver Cancer Marker Test
4. Screening for Liver Fibrosis:
- Apolipoprotein
- Total bilirubin
- GGT
- Alpha2-Macroglobulin
- Haptoglobin
5. Annual Health Check-Up: Regular comprehensive health check-ups to monitor overall liver health and detect any early signs of liver disease.