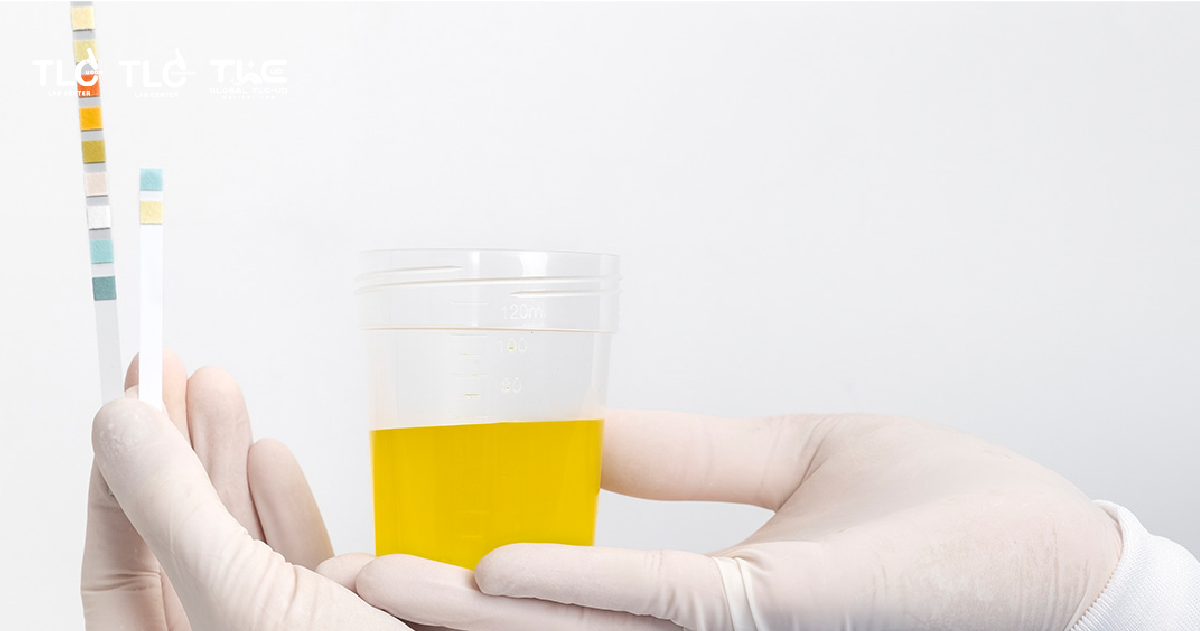
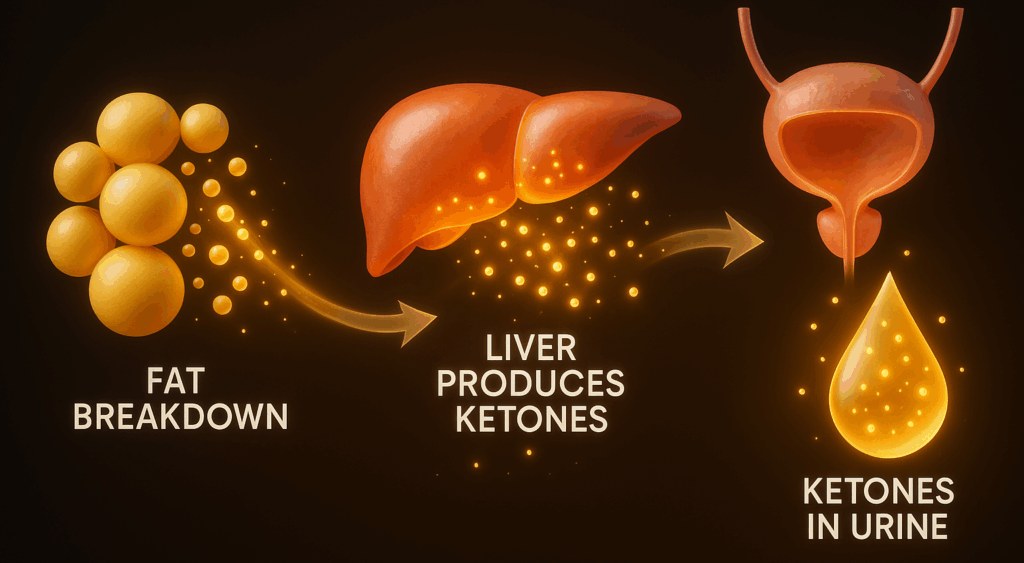
Ketones are chemicals produced by the liver when the body breaks down fat to use as energy. Normally, the body relies on glucose from food as its main energy source. However, when glucose levels are too low, the body switches to burning fat instead, leading to the production of ketones, which are excreted in the urine.
A positive ketone urine test means the level of ketones in your urine is higher than normal.
Why Do Ketones Appear in Urine?
- Diabetes
- Most commonly seen in people with diabetes, especially type 1 diabetes
- High ketone levels may indicate insufficient insulin, causing the body to burn fat instead of sugar
- This may be an early warning sign of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) — a serious and potentially life-threatening complication
- Fasting or Malnutrition
- Skipping meals, eating very low-carb diets, or having an eating disorder can cause the body to break down fat for fuel and produce ketones
- Prolonged Exercise
- After long or intense workouts, the body may switch to burning fat, resulting in detectable ketones in urine
- Illness or Physical Stress
- Conditions like high fever, infections, or other physical stressors can trigger the body to produce more ketones, especially when appetite is reduced
Symptoms of High Ketone Levels
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Fatigue or weakness
- Excessive thirst
- Frequent urination
- Fruity-smelling breath
What to Do If You Have Ketones in Your Urine
- If you have diabetes, especially type 1:
- Check your blood sugar immediately
- See a doctor immediately if you feel unwell, your blood sugar is high, or you notice any signs of DKA (diabetic ketoacidosis).
- Stay hydrated and try to eat regularly
- If you’re not diabetic and are feeling well, ketones may be due to:
- Skipped meals
- Fasting
- Intense physical activity
Lab Tests to Consider
Blood and urine tests may include:
- Fasting blood sugar
- HbA1C
- Urine ketones
References
- MedlinePlus. (2022). Ketones in urine. U.S. National Library of Medicine. [ medlineplus.gov ]
- StatPearls. (2024). Ketonuria. StatPearls Publishing. [ ncbi.nlm.nih.gov ]