Get to know malaria, trembling fever or wild fever
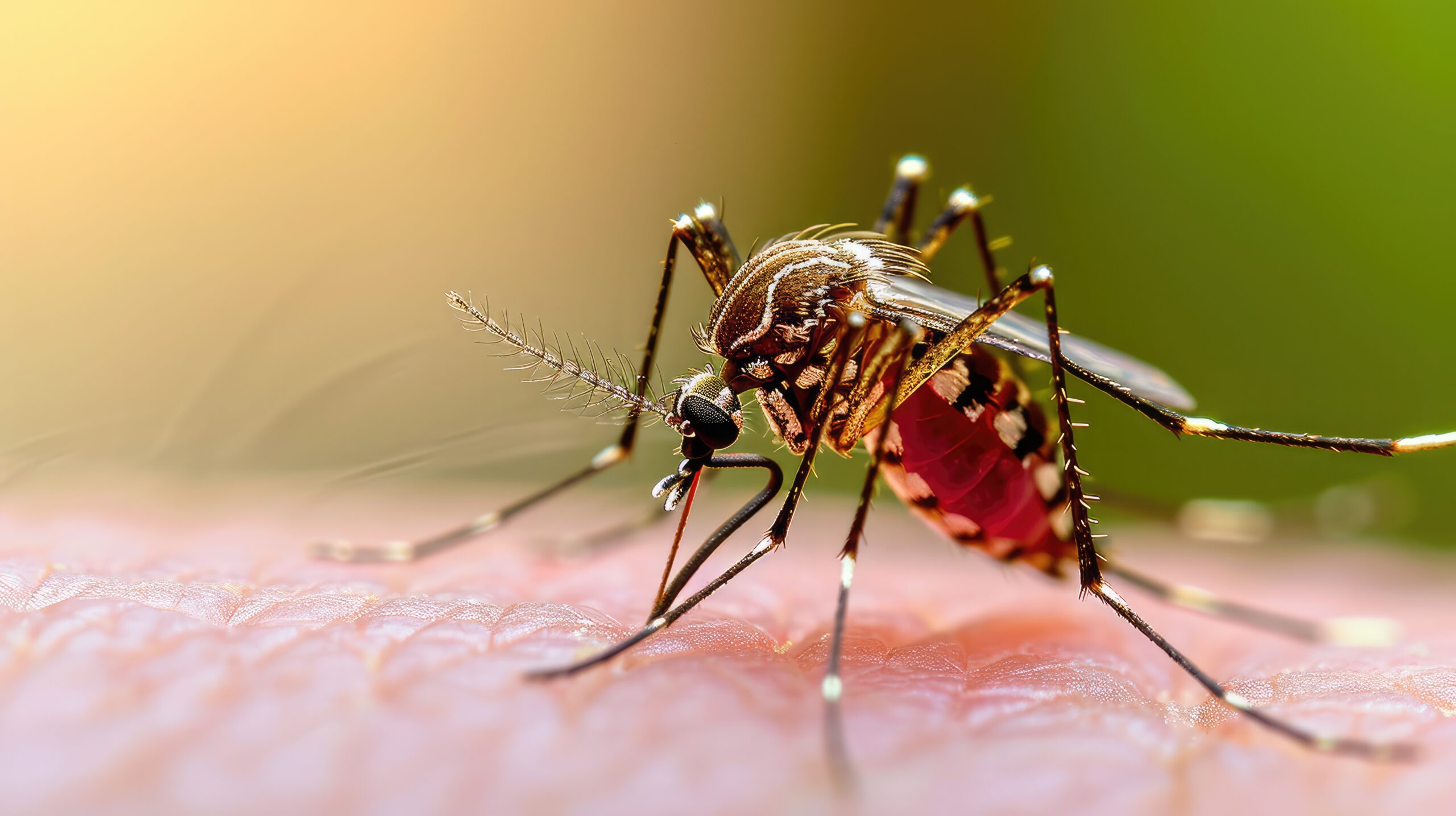
Malaria is a disease caused by protozoa carried by female Anopheles mosquitoes. This causes the patient to have a high fever and chills. The disease is often found in tropical countries and areas that are naturally waterlogged.
There are 5 types of malaria that cause disease in humans :
- Plasmodium falciparum (P.f.) is a severe infection. If you are seriously ill, you may develop malaria in the brain. If not treated in time, it can lead to death.
- Plasmodium vivax (P.v.) It is a mild type of infection, but if not cured. The infection can stay in a person’s body for many years, causing the symptoms of malaria to come and go.
- Plasmodium malariae (P.m.)
- Plasmodium ovale (P.o.)
- Plasmodium knowlesi (P.k.) It is a malaria infection that is present in macaques and then cross- infects humans.

Contagiousness of the disease
When female Anopheles mosquitoes carry malaria infection onto humans, they release malaria from their salivary glands into the bloodstream.
Incubation period of the disease
- Plasmodium falciparum (P.f) The incubation period is about 7-14 days.
- Plasmodium vivax (P.v) and Plasmodium ovale (P.o), the incubation period is about 8-14 days.
- Plasmodium malariae (P.m) The incubation period is about 18-40 days.
Malaria life cycle
Malaria progresses through two growth stages:
- Mosquito phase : This phase begins when female mosquitoes bite and suck blood from individuals infected with malaria. These mosquitoes carry malaria parasites in their developmental stage. The parasites enter the mosquitoes and reproduce, producing larvae that embed themselves in the mosquitoes’ stomachs. Subsequently, they divide and migrate to the mosquitoes’ salivary glands. When mosquitoes bite humans and release saliva to prevent blood clotting, they also transmit malaria parasites into the human bloodstream.
- Human phase : Once malaria parasites enter the bloodstream, they travel through blood vessels to liver cells. There, they multiply until they reach a certain stage when they break out of liver cells. These parasites then invade red blood cells, where they continue to multiply until the red blood cells rupture. The parasites then invade other red blood cells for sustenance. This cycle of growth and division occurs continuously. Some parasites undergo a transformation into male or female parasites. At this stage, patients begin to exhibit symptoms of the disease, including fever, chills, and headache. Malaria parasites can be detected in the blood during this phase.
For Plasmodium Vivax, some of them temporarily pause growth. After some time, it can resume growth, which causes the recurrence of fever and malaria.
Outbreak source
Malaria is a tropical disease that is prevalent in Africa, South America, Asia, and the islands of the Pacific Ocean. In some countries, especially in Africa, malaria infections are a high risk, so always consult a doctor before traveling because in some cases, malaria prevention medication may be necessary.
In Thailand, malaria outbreaks are in border provinces, especially in mountainous areas, dense forests, and water sources7 and streams that are breeding grounds for Anopheles mosquitoes. Provinces where the majority of malaria patients are found include Mae Hong Son, Tak, Trat, Ranong, Kanchanaburi, Chanthaburi, Sa Kaeo, Prachuap Khiri Khan, Ratchaburi and Chumphon.
Symptoms of malaria :
During the initial stages of infection, patients will have flu-like symptoms, including fever, headache, aches, nausea, and loss of appetite. Symptoms for each patient may vary according to their immune system. As for the specific symptoms of malaria, nowadays they are not often the same as in the past. Some patients may experience mild symptoms, but some cases may be so severe that they are the leading cause of death from various complications.
Severe and life-threatening complications:
- Anaemia Malaria infection causes red blood cells to be destroyed. This results in decreased oxygen transport to the muscles and vital organs of the body.
- Cerebral malaria infection can affect the brain. May cause weakness, seizures, or critical symptoms.
- Pulmonary oedema causes fluid accumulation in the lungs, causing breathing difficulties.
- Failure of internal organs such as the liver, kidneys, or spleen.
- Low blood sugar, hypoglycaemia.
- Acute respiratory failure
- Shock due to a sharp drop in blood pressure
Disease prevention and control
- Prevent mosquito bites by sleeping under a mosquito net or a mosquito net moistened with mosquito repellent, or apply mosquito repellent direct to the skin.
- Destroy mosquito breeding sites. such as waterlogged areas.
- Avoid entering areas with high disease transmission. If necessary, take preventive medication before entering the area, and once you come out, take a blood test for infection.
- Workers or groups of people moving from neighbouring countries must be tested and treated if found to be infected.

Laboratory tests
- Malaria Antigen
- Thick and thin film staining.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC)
References
- Hospital for Tropical Diseases. (2020). มาลาเรีย ไข้จับสั่น หรือไข้ป่า (Malaria). tropmedhospital.com
- Global Health, Division of Parasitic Diseases and Malaria. (2024, April 9). Malaria. cdc.gov
- Phillips, M., Burrows, J., Manyando, C. et al. Malaria. Nat Rev Dis Primers 3, 17050 (2017). doi.org