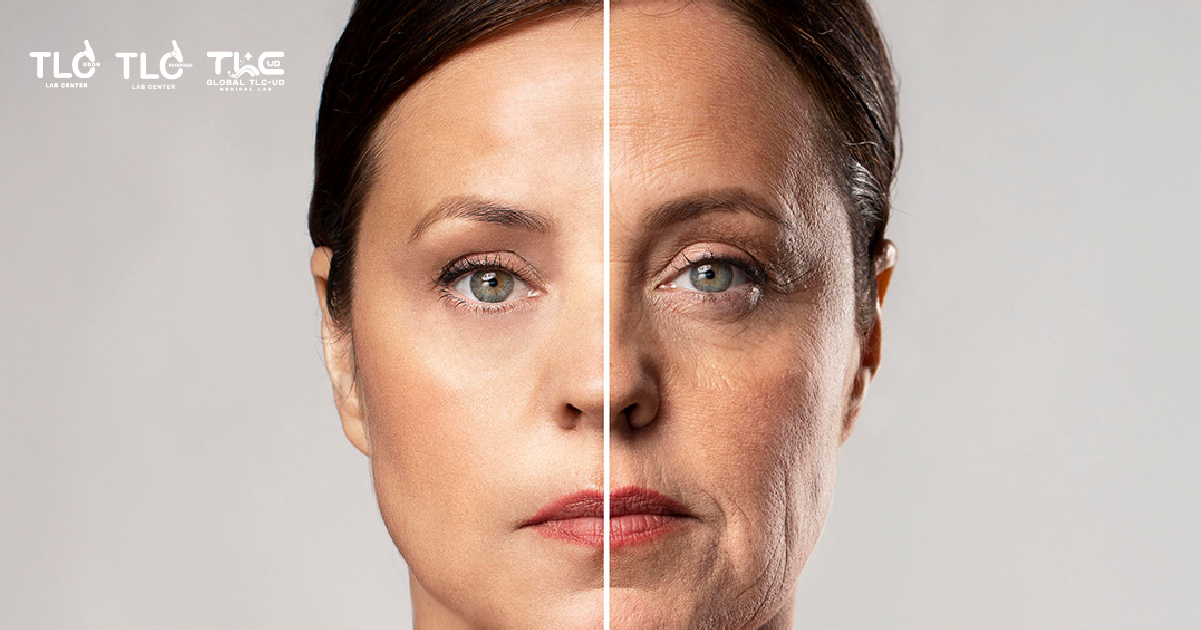
What is NAD+?
NAD+ or Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide is a type of coenzyme that the body can synthesize naturally. A coenzyme is a small molecule in the body that stimulates the work of enzymes. Important coenzymes include vitamin B, vitamin C, and coenzyme Q10 which helps converts food into energy.
NAD+ coenzyme can be found in cells, promoting cell proliferation and converting cell energy into important compounds for the human body. It repairs cells and improves cellular metabolism while slowing down the aging process and various age-related diseases.
NAD+ is the ultimate in anti-aging, health care and slowdown of brain degeneration and is one of the most important molecules in the body which can be found in all types of living cells.
With age, the amount of NAD+ coenzyme in the body gradually decreases, leaving insufficient to maintain a proper balance in the body. As we enter middle age, NAD+ levels drop to only 50% and gradually decrease to 1%-10% as we reach old age. It is of such importance that our lives can end in minutes without NAD.
How is vitamin B3 different from NAD+?
Vitamin B3 , or Niacinamide, in nature is converted into Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide or NAD+. NAD+ is a very important enzyme in almost every chemical process of the body, including metabolism, fatty acid production, and free radical destruction – which is one of the major causes of old age.
Most importantly, NAD+ is a precursor to gene or DNA repair. Muscle cells, white blood cells, and even pancreatic cells work well because of it.
Therefore, NAD+ is important to almost every system in our body. Generally, if our body does not get enough vitamin B3 our system will try to replace it by using the essential amino acid Tryptophan to convert it into NAD+. The body cannot synthesize it. We then need to take supplements to provide the body’s needs.

How NAD+ works
- It is a source of energy synthesis for cells in the body.
- It is used to treat Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and degenerative diseases of the nervous system.
- Improves the performance of the immune system
- Helps slow down degeneration at the cellular level by increasing telomere length.
- Stimulates DNA repair
- Helps activate Sirtuin proteins (genes that control cell aging.)
- Helps the heart muscle to work better for the benefit of the cardiovascular system
NAD + Why is it necessary?
As we age, organs degenerate over time, and the gradual decline of NAD+ will affect cellular function, including:
- accelerated skin sagging,
- Increased work aches and pains
- Increased weight gain even with the same amount of food consumed
- Short-term forgetfulness – even things I used to remember well.
- Frequent discomfort or susceptibility to illness
These symptoms are caused by daily lifestyle as a result of the continuous deterioration of NAD+ in the body. In addition, when hypothyroidism occurs, NAD+ affects the functioning of various body systems, such as:
- Dementia and neurodegeneration.
- Muscular disorders.
- Cardiovascular diseases.
- AIDS.
- Diabetes.
- Obesity.
- Infertility.
- Inflammation of the body.
Thus, maintaining health and slowing down degeneration at the cellular level is so important. This can be done by increasing the amount of NAD+ in the body, which will contribute to the efficient functioning of cells in the body because it stimulates two important health aspects: converting food into energy and regulating the cells to function well.
Who is suitable for NAD+ supplementation?
- Health lovers who want to slow down the deterioration of the body.
- Those who want to restore the functioning of the nervous system.
- People who suffer from declining brain function.
- Those who want to restore strength and muscle function.
- Those who want to accelerate their weight loss program.
- People who work hard or who have chronic fatigue syndrome.
- People who need help to strengthen vision.
Preventative health care is required to slow down cell degeneration and reduce deterioration of the body in order to alleviate the severity of illnesses that may occur and to help strengthen health.
References:
Braidy, N., & Liu, Y. (2020). NAD+ therapy in age-related degenerative disorders: A benefit/risk analysis. Experimental Gerontology, 132(110831).
Hong, W., Mo, F., Zhang, Z., Huang, M., & Wei, Z. (2020). Nicotinamide mononucleotide: A promising molecule for therapy of diverse diseases by targeting NAD+ metabolism. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 8(246), 27 pages.
Hong, W., Mo, F., Zhang, Z., Huang, M., & Wei, Z. (2020). Nicotinamide mononucleotide: A promising molecule for therapy of diverse diseases by targeting NAD+ metabolism. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 8(246), 27 pages.