Probiotics and Prebiotics: How important are they for good digestive health?
Good food selection is beneficial to the body. Choose food that is easily digested and freshly cooked. and eat it at the correct time. Eating foods that contain good microorganisms called “Probiotics” is another option that will help take care of our digestive system. This is not only Probiotic that we should get to know, but also Prebiotic, an important partner… and very popular in taking care of all of our digestive health.
Probiotic and Prebiotic have similar names but they are not the same thing.
If we talk about Probiotics, some people may have heard of them before. But when faced with the word “Prebiotic,” many people may be confused and think that it may be the name of the same thing with the same meaning.

What are probiotics?
Probiotics are living things. It is the name of small microorganisms that live in the human body with good bacteria (normal flora) whose function is to help digest and protect our digestive system, producing substances to resist or eliminate undesirable microorganisms. In addition to probiotics, they are already present in our bodies, and can also be found in some products such as fermented foods and dietary supplements.
What are prebiotics?
Prebiotics are non-living things that the body cannot digest and absorb in the small intestine. These are sent to the large intestine… and are broken down by microorganisms called Probiotics, or – to put it simply – Prebiotics are the food of the Probiotics that help the Probiotics grow well. They are found in foods such as carbohydrates and dietary fibre.
Prebiotics should be taken together with the prebiotic.
Prebiotics are good food that is beneficial to probiotics. These two things should be added to the body at the same time in order for the probiotic to work at its full potential. Food groups that contain the probiotics that we often hear about include milk, yogurt, or pickles. Food groups that are high in prebiotics include garlic, cabbage, avocados, and bananas.
Probiotics: How are these types of microorganisms good for the digestive system?
Solve gastrointestinal problems such as diarrhoea, constipation, irritable bowel syndrome, or chronic ulcerative colitis.
Helps produce vitamin K and short-chain fatty acids.
- Stimulates the digestive system by producing various enzymes.
- Helps maintain oral health and prevent tooth decay.
- Prevent allergies. Helps stimulate the immune system to reach a balanced state.
- Helps reduce blood pressure.
- Prevents bacterial infection.

What should I eat to add probiotics?
- Natural yogurt, flavoured curd : Yogurt with probiotics clearly indicated on the product label, such as Active Probiotics, Live biopics, probiotics that help the digestive system, such as Lactobacilli and Bifidobacterium.
- Kefir is the same type of fermented milk as yogurt, but using different fermented microorganisms. Contains probiotics, as well as yogurt.
- Kimchee Pickles: When vegetables are marinated for a while, probiotic microorganisms are produced.
- Fermented tea
- Natto: Natto beans or Japanese rotten beans are considered probiotic sources and help prevent heart disease and osteoporosis.
- Some types of cheeses: Note that these are cheeses that state they have live culture or active culture, such as Mozzarella, Cottage and young Cheddar cheese.
- Dark chocolate in which Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium probiotics are found.
What are the prebiotics in the diet?
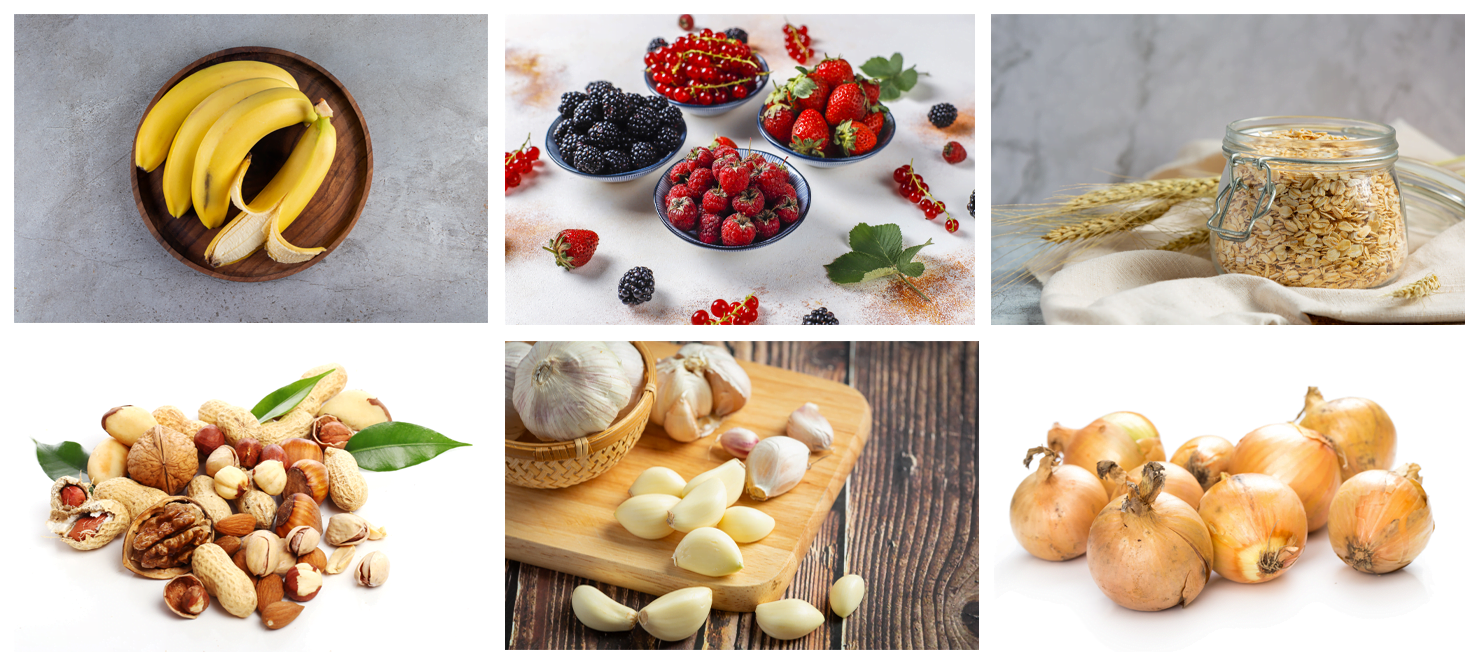
They are found in foods that are high in fibre such as:
- bananas
- berry fruits
- oats
- beans
- garlic
- asparagus
- onion
- spring onions (scallions)

The digestive tract is just as important as other body systems, so we should take care of it at all times. If neglected until a disorder occurs, do not forget that we cannot see its internal health.
Reference :
- Department of Gastroenterology. “Prebiotic diet – FAQs” [Online]. Available from: monash.edu
- Dhipayanet Ariyapitipan. “Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Symbiotic and Human Health.” Journal of the Dietitian Association of Thailand. 40, 1-3 (2563): 107-110.