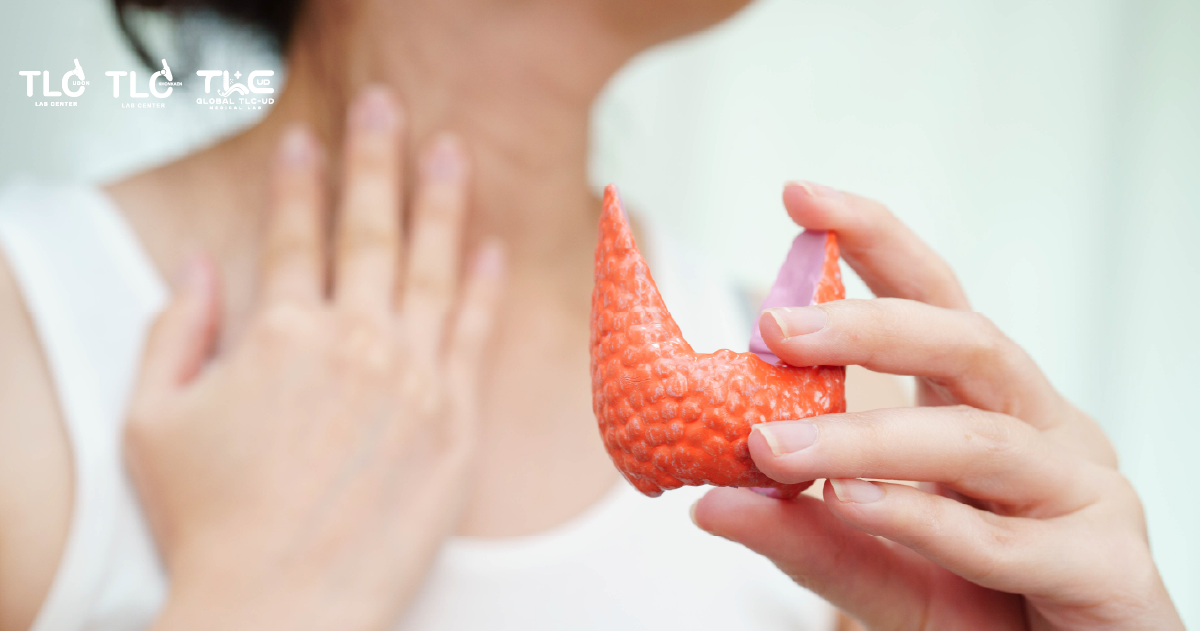
What is the thyroid gland?
It is the largest endocrine gland in the body, located in the front part of the neck resembling a butterfly’s wings. Its function is to produce thyroid hormones and release them into the bloodstream to act on various organs in the body under the control of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus gland. The production of thyroid hormones requires iodine as a component. If there is too much or too little iodine, it can cause the thyroid to malfunction and affect almost every system in the body.
Important functions of thyroid hormone
- Related to body growth. and various organs
- Related to the functioning of the brain and nervous system. including emotional states
- Related to the body’s metabolic system. temperature control
- Involved in the functioning of many organs such as muscles, heart, and bones.
However, if the body has higher hormone levels than normal. It will stimulate the various systems of the body to work more. This condition is called “hypothyroidism” and is dangerous to health.
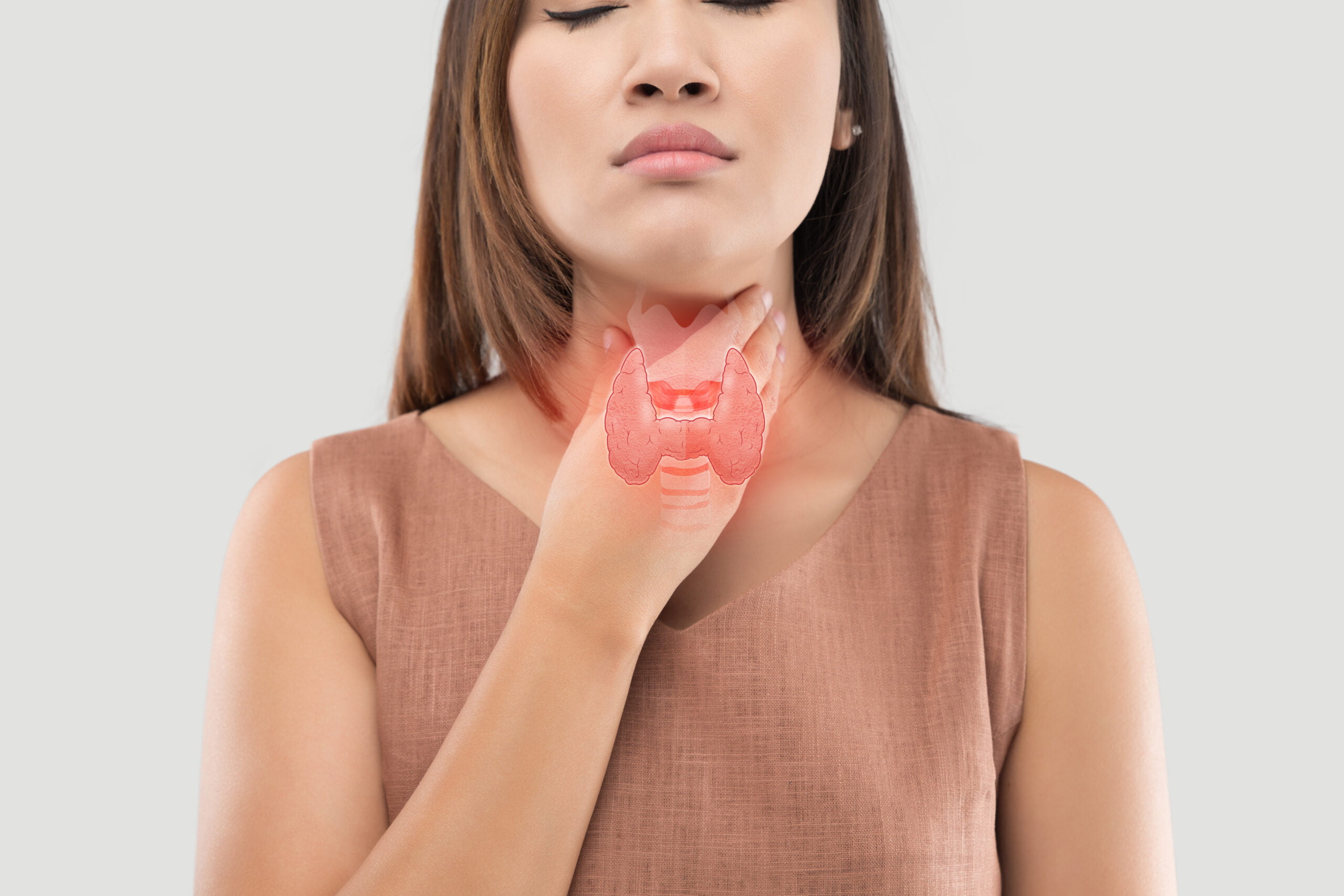
Thyroid toxicity. What are the symptoms?
Each patient may have different thyroid symptoms. Some people have no symptoms. Some people have clear symptoms. and may become severe to the point of crisis. This is because thyroid hormones stimulate the functioning of many body systems. Each patient has a variety of symptoms as follows :
Cardiovascular system
- Tired easily.
- Rapid heartbeat.
- Heart palpitations.
- Arrhythmia.
- May even lead to heart failure.
- Nervous system
- Hands shake.
- Easily irritated.
- cannot sleep
- restless
- Lack of concentration.
- Skin system
- excessive sweating
- clammy skin
- hair loss, baldness
- thick skin on the shins
- fingers and nail erosion.
- Eye system
- Eyes enlarge
- eyelids wide open, or eyes may bulge.
- Gastrointestinal system
- often hungry
- frequent bowel movements
- loose stools
- nausea and vomiting
- Metabolic system
- Weight loss even if you eat normally or eat a lot.
- Body warms up.
- Reproductive system
- Menstruation is irregular. A little bit Missed menstruation
- infertility
- Muscular system
- weakness
- trembling hands
- Neck
- An enlarged neck.
- Some people may have a lump on the thyroid.

Causes of thyroid poisoning
- The thyroid produces more hormones.
- Thyroid inflammation releases a lot of stored hormones.
- Overdose of thyroid hormone from medications or combinations in certain supplements.
- Taking certain medications
- Severe morning sickness or ovarian tumours produce a lot of thyroid hormones.
- Pituitary tumours produce thyroid-stimulating hormones, but they are very rare.
There are 2 types of thyroid poisoning.
- Toxic enlargement or hyperthyroidism or thin thyroid, which can be divided into 3 types:
- Graves’disease
- Toxic multinodulal
- toxic nodule.
Hypothyroidism or obese thyroid is a condition that is the opposite of hyperthyroidism, which is that thyroid hormones in the blood are too low and cause abnormal symptoms in the body.
Difference between Hyperthyroid and Hypothyroid
Hypothyroidism : This is a condition in which the body has low levels of thyroid hormones, so it burns less energy than normal and has symptoms such as:
- Sluggish, bored, lazy I don’t want to do anything.
- Frequent sleepiness, cold Hair loss
- Weight gain, puffy fat
- I get tired easily, I can’t do anything.
- constipation
- Some people have irregular periods.
Hyperthyroid : It is a condition in which the body has high levels of thyroid hormones and therefore burns more energy than usual.
- Heart palpitations, hands shaking, excitement, easily startled.
- Feeling hot, sweating a lot.
- Angry and irritable. Easily stressed
- Frequent hunger. Eating well, but no weight gain
- Gets tired easily
- Less menstruation
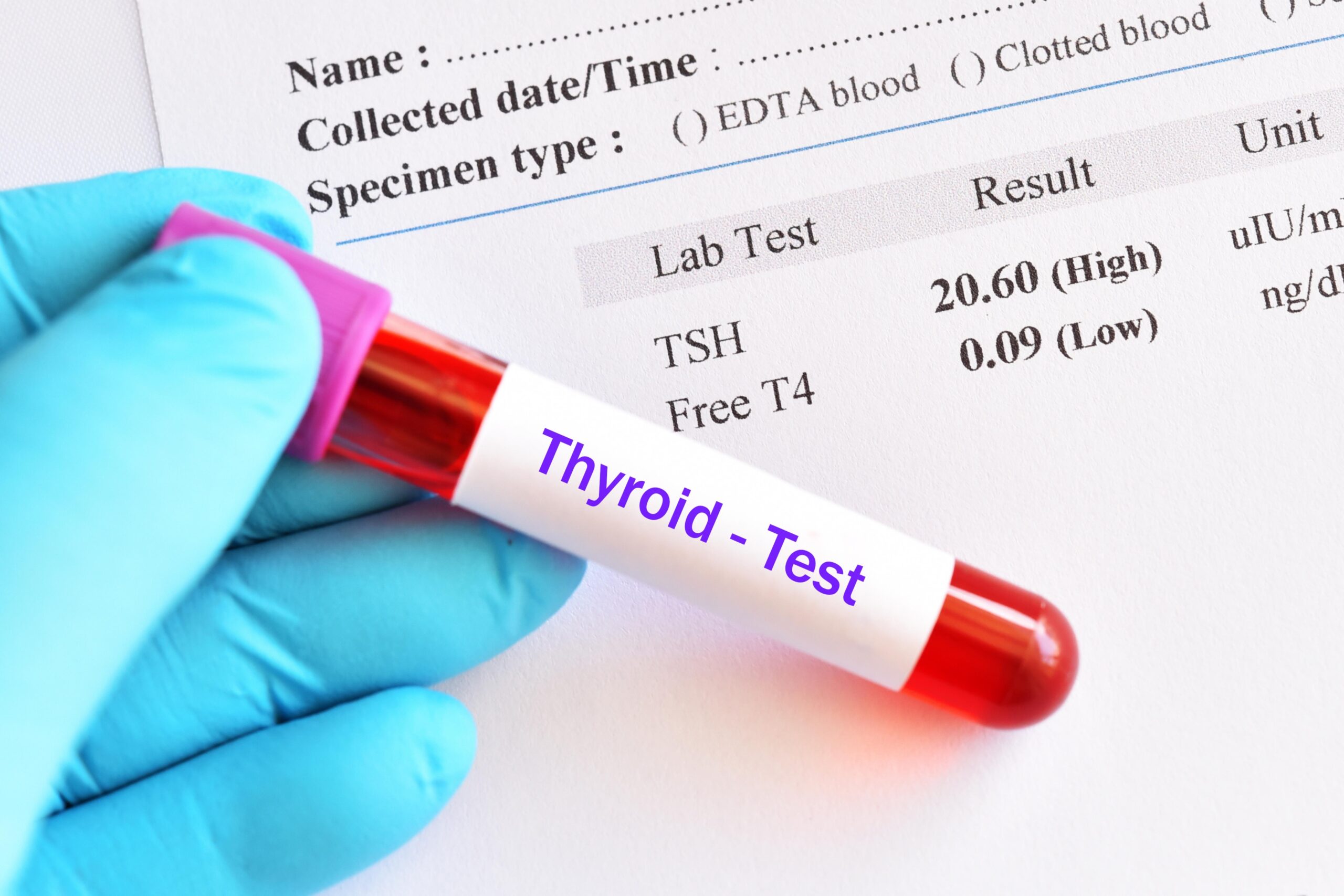
Laboratory analysis to check thyroid disease risk
Blood test to measure thyroid levels, such as
Thyroid Function
- FT3
- FT4
- TSH
Health Check-up Program for Thyroid Function <<Click here for details>>