Calcium is a vital mineral and the most abundant in our body. About 99% of it is found in bones and teeth, where it helps increase bone density and keeps them strong. The remaining 1% is in the bloodstream and various tissues, playing important roles in regulating organ functions, like muscle contractions, heartbeat, blood clotting when you get injured, nervous system activity, and activating several enzymes.
Not Enough Calcium? Risk of Osteoporosis.
When your body doesn’t get enough calcium, it starts pulling calcium from your bones to keep essential processes going. If this happens often, bones can become porous and brittle, making them weaker and more prone to breaking, even from minor impacts.
Recommended Calcium Intake for Different Age Groups
Based on the 2020 Thai Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs), here’s how much calcium people should get by age and gender:
- Children 1-3 years: 500 mg/day
- Children 4-8 years: 800 mg/day
- Teenagers 9-18 years: 1,100 mg/day (During adolescence, about 40% of bone mass is built, so getting enough calcium is extra important.)
- Adults 19-50 years: 800 mg/day (For women, once menopause hits, estrogen drops, which leads to faster bone loss, so women are more at risk for osteoporosis and fractures than men, who don’t have a sudden hormone drop.)
- Adults 51 and up: 1,000 mg/day
- You should get enough calcium, but not more than 1,500 mg/day
What Helps Calcium Absorption?
- Vitamin D: This vitamin boosts the production of proteins in the gut lining that grab onto calcium and pull it into the bloodstream. You get vitamin D from sunlight and foods like fish, egg yolk, liver, and butter.
- Mildly acidic foods: Calcium dissolves better in mildly acidic conditions.
- Lactose: The sugar in milk can improve calcium absorption by 15-50%, so regular milk is a good calcium source.
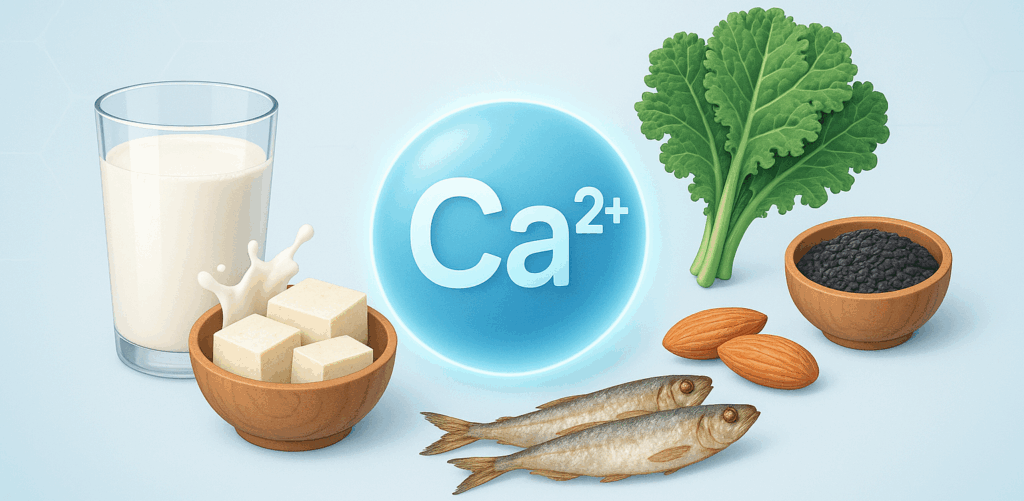
Best Calcium Sources
- Milk and dairy products (from animals) are the best sources, high in calcium and with a good calcium-to-phosphorus ratio for absorption (milk, yogurt, cheese).
- Plant-based milks (like soy milk) usually have less calcium, so pick types that are calcium-fortified, and check the label for at least 20% of the daily recommended calcium per serving.
- Small fish and edible bone-in seafood (anchovies, sardines, dried shrimp, etc.).
- Tofu (yellow, firm, or dried tofu skin).
- Edamame and black sesame seeds.
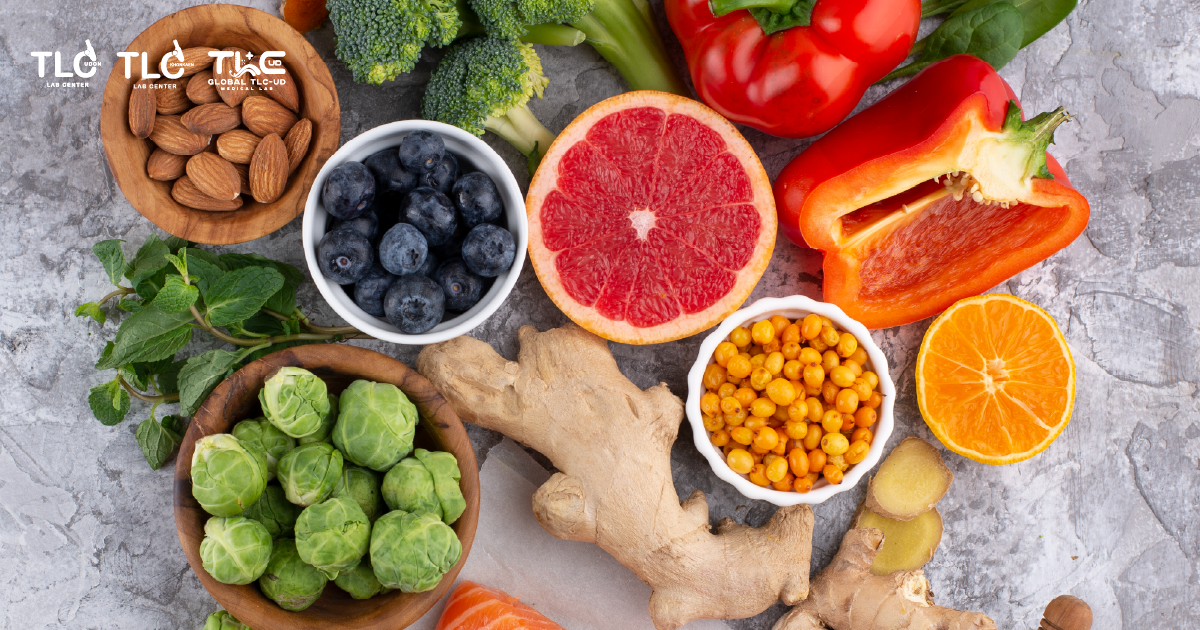
- Green leafy veggies that are medium-to-high in calcium but low in oxalates (which can block absorption), like kale, Chinese cabbage, cassia leaves, ivy gourd, gotu kola, and winged bean.
How to Lower Your Risk of Osteoporosis?
- Don’t eat too much animal protein.
- Avoid salty foods, too much sodium makes you pee out more calcium.
- Don’t overdo caffeine (tea, coffee), it can also increase calcium loss in urine.
- Cut down on soft drinks, they have lots of phosphorus, which can mess with calcium balance in your blood.
- Limit alcohol, alcohol blocks calcium absorption and increases its loss in urine. Heavy, regular drinking will lower your calcium.
- Don’t smoke, nicotine gets in the way of your body using calcium properly.