Let’s first get to know the hormone insulin. Insulin is produced by the pancreas and helps transport sugar into cells, where it is converted into energy. Excess sugar is stored as glycogen and fat for future energy needs. Insulin resistance occurs when the body produces less insulin or when insulin function is impaired. This condition is common in overweight individuals, particularly those with high abdominal fat. Insulin resistance leads to elevated blood sugar levels, which can cause type 2 diabetes.
What is insulin resistance?
Insulin resistance is a condition in which cells in the body respond less well to insulin than normal, resulting in poor sugar absorption into cells. Blood sugar rises and leads to type 2 diabetes, so that when the cells response to less insulin, the body mechanism stimulates the pancreas to produce more insulin so that the cells can draw insulin to extract enough glucose or blood sugar and normalize blood sugar balance. Especially in people with obesity or overweight, high blood sugar levels are not detected, but if this mechanism is allowed to stimulate the pancreas to work hard to produce insulin for a long time to maintain blood sugar balance, the pancreas will deteriorate to the point that it produces less insulin. Then the risk of diabetes will immediately follow.
Symptoms of insulin resistance
People with insulin resistance might not have noticeable symptoms, so they may be unaware of their condition. It is often only discovered when they develop type 2 diabetes or through a blood test indicating elevated blood sugar levels consistent with diabetes. Common symptoms of diabetes includes:
- Frequent hunger, which may mean feeling hungry between meals, or being abnormally thirsty.
- Frequent or over-abundant urination
- Abnormal fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Numbness in the feet
- Skin symptoms such as skin tags and Acanthosis nigricans, which are thick and rough black skin crusts often found on the back of the neck, armpits, and groin.
Many people wonder if they are having a problem with insulin resistance. Factors that affect the development of insulin resistance includes:
- Increased body weight, fattiness, or visceral fat.
- High blood sugar levels/high accumulated sugar.
- Have high triglyceride values in the blood after fasting for at least 10 hours.
- Low HDL cholesterol
- High LDL cholesterol
- There are other diseases associated with the risk of insulin resistance, such as fatty liver, and post-menopausal ladies may have hormone changes.
How is insulin resistance diagnosed?
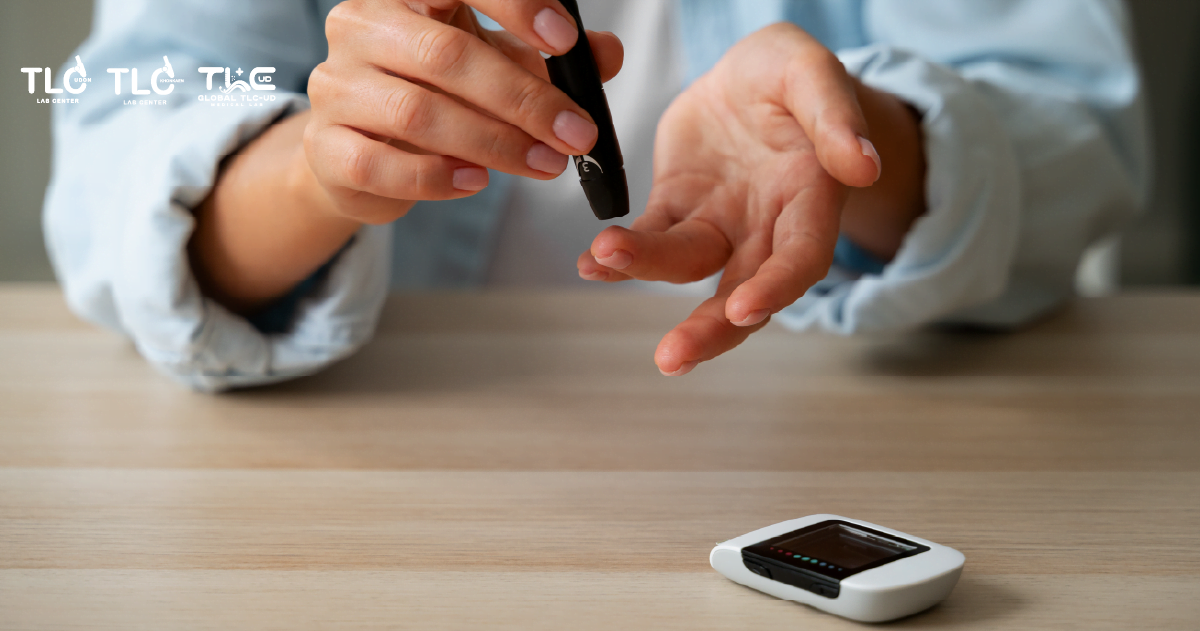
1. A blood test can be performed to check the level of insulin in the fasting phase (Fasting Insulin) after fasting for at least 10-12 hours.
This test primarily measures insulin resistance in the liver. While it cannot directly assess insulin resistance in muscle tissue, we are able to indicate the presence of insulin resistance in the body by a very high fasting insulin level when considered alongside other health data.
2. Homeostasis Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR)
A HOMA-IR value can assess both insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) and insulin secretion (HOMA-Beta) using insulin and glucose levels measured after fasting for at least 8 hours.
A HOMA-IR score can be calculated by using this formula:
(Glucose x Insulin)/405
A HOMA-IR value greater than or equal to 2.0 indicates potential insulin resistance. If the value is higher than 2.0, further testing, such as the Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (75 gm OGTT), should be conducted to confirm the diagnosis.
Prevention of insulin resistance
- 1. Control your daily energy intake and choose foods wisely. Avoid foods and drinks high in sugar and fat, such as coffee with added sugars, iced milk tea, bubble tea, soft drinks, processed flour products, baked goods, crunchy snacks, and fried items like curry puffs, pa tong go, and rice cakes.
- Moderate weight BMI <23 Kg/m2
- Exercise regularly, for at least 30 minutes at a time, at least 3 times a week.
- Refrain from all kinds of alcoholic beverages.
An annual health check-up promotes health and helps prevent diabetes, a disease that can lead to numerous complications, including cardiovascular disease, stroke, kidney disease, and Alzheimer’s.