What are micronutrients? And why are they important for the body?
Micronutrients :
They are small molecule nutrients that the body needs in small amounts, such as vitamins, minerals and nutrients from fruits and vegetables, also known as phytonutrients. Together, these nutrients support various functions and are very important for the body.
Why are micronutrients important?
These vitamins and minerals perform a variety of functions, including helping the body produce enzymes, hormones, and other substances necessary for the body’s normal development.
Why do we need to get tested for micronutrients?
It is a nutritional examination of the body in order to make a nutrition plan or take care of vitamins individually. The checklist is as follows:
What does a micronutrient consist of ?
Micronutrients Profile:
- Vitamin A (Retinol)
- Vitamin B12
- Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid)
- Vitamin D2
- Vitamin D3
- Vitamin E (Gamma-Tocopherol)
- Vitamin E (Alpha-Tocopherol)
- Lutein + Zeaxanthin
- Beta-Carotene
- Lycopene
- Alpha-Carotene
- Beta-Carotene
- Coenzyme Q10
- Chromium
- Copper
- Selenium
- Zinc or Zinc
- Magnesium
- Folate
- Ferritin
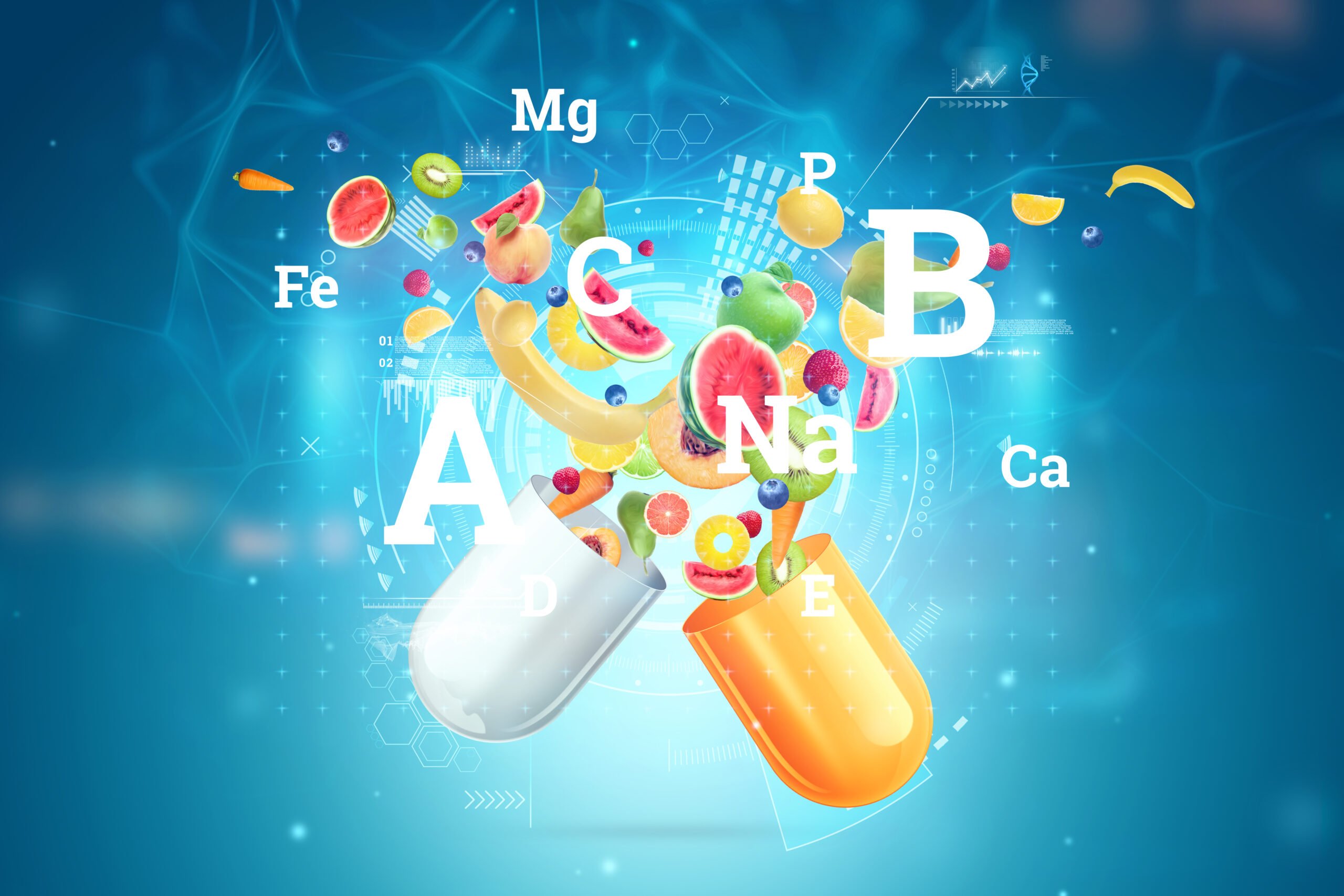

Benefits of individual vitamins and minerals
- Vitamin A
- It is a type of fat-soluble vitamin that is important for the immune system, reproductive system and vision. If the amount is not enough to meet the body’s needs, there is a risk of eye problems: dry eyes, blindness and other infections.
- Vitamin B12
It is a water-soluble vitamin. Its important to help in the production of healthy red blood cells and DNA. Vitamin B12 deficiency can affect memory and cognition. Reduces fatigue, prevents eye deterioration. The risk of vitamin B12 deficiency increases for vegetarians.
- Vitamin C
- It is a water-soluble vitamin that is important in preventing immune system diseases. It supports the cardiovascular system, and iron absorption. Vitamin C also affects tissue formation, wound repair, and affects the health of cartilage and bones.
- Vitamin D2/D3
- Vitamin D2 is present in plants and yeast, while D3 comes from animals. The human body is able to produce vitamin D when exposed to sunlight. Vitamin D plays an important role in maintaining bone mass, and the nervous and immune systems. We can get vitamin D from sunlight, food, and vitamin supplements
- Vitamin E Gamma – Tocopherol)
- It has anti-inflammatory properties. Anti-aging, anti-cancer, heart disease, Alzheimer’s disease and age-related decline.
- Vitamin E (Alpha – Tocopherol)
Helps support the heart, blood circulation, and immunity. Helps keep skin healthy.
- Lutein
- It is a carotenoid compound that gives yellow and red colours to plants, which are anti-oxidants providing outstanding freedom in eye health protection from the destruction of free radicals and UV light or even blue light. We can find a lot of this substance on the retina, since it has the ability to absorb excess light that enters the eyes, thus preventing macular degeneration. It is found in dark leafy green vegetables such as kale, coriander, spinach, and broccoli.
- Zeaxanthin
- It is another carotenoid compound found mainly on the retina, protecting the eyes. It is often found along with lutein, and also has the ability to protect the skin from damage from the sun (UVB). It too is found in dark leafy green vegetables such as kale, coriander, spinach, and broccoli.
- Beta – Cryptoxanthin
- It is a substance belonging to the group of carotenoids, a precursor of vitamin AT, which the body can absorb and use well (bioavailability), helping to reduce the risk of lung and colon cancers, and help prevent inflammation of the body, especially inflammation that affects the risk of rheumatoid arthritis. It is found mainly in mandarins, persimmons, oranges, papayas, and pumpkins.
- Lycopene
- It is an antioxidant that gives red colour in plants, protects cells from damage by anti-free radicals. It reduces the risk of abnormal cell division or cancer cells. It is found in red and pink fruits such as tomatoes, watermelons, and pink grapefruits.
- Alpha Carotene
It belongs to the carotenoid group and is a precursor of vitamin A, like beta-carotene, although the absorption rate is less. It reduces the growth of abnormal cells or cancer cells such as lung cancer, and prostate cancer.
It is found in pumpkins, watermelons, cantaloupe melons, carrots, ripe mangoes, and beetroot.
- Beta Carotene
It is a group of pigments that give orange and yellow colours and belongs to the carotenoid group, which is a precursor of vitamin A, making it beneficial for the immune system and general health. It is also an antioxidant. It protects the body from degeneration.
It is found in pumpkins, watermelons, cantaloupe melons, carrots, and ripe mangoes.
- Coenzyme Q10
- It is an antioxidant that is abundant in the mitochondria of cells. It helps cells generate energy, nourishes the heart. and regulates blood sugar levels, helps prevent cancer, and reduces the frequency of migraines. It can also reduce oxidative damage that causes muscle fatigue, skin damage and brain and lung diseases Found in deep sea fish, spinach, broccoli, black sesame seeds and pistachio nuts
- Magnesium
- Magnesium is important for various processes in the body, helping muscles and nerves function normally. Maintains optimal blood sugar and blood pressure levels and help the body make protein, bones, and DNA.
- Magnesium deficiency risks the development of symptoms such as headache, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and weakness
- Severe magnesium deficiency can cause numbness. Muscle pain, seizures, irregular heartbeat and also the risk of high blood pressure, heart arrhythmia, type 2 diabetes, and osteoporosis.
- Magnesium is important for various processes in the body, helping muscles and nerves function normally. Maintains optimal blood sugar and blood pressure levels and help the body make protein, bones, and DNA.
- Folate
- It is a B vitamin essential for the production of red and white blood cells in the bone marrow. It builds DNA and RNA and converts carbohydrates into energy. Having adequate amounts of folate is especially important during periods of rapid growth, such as pregnancy, infancy and adolescence. In adults, it helps to nourish the blood.
- Ferritin
- It can show that the body has too much or too little iron, or it can be used to diagnose other diseases.
Why should we check micronutrients?
A lack of these nutrients can cause dangerous health problems, which can lead to an impact on overall ability. It may degrade performance, and increase the risk of diseases and other health conditions.
We can prevent these nutritional deficiencies through correct nutrition knowledge and the consumption of a variety of healthy foods, as well as taking supplements where necessary.
Who is suitable for a Micronutrient Profile?
Micronutrient examination is suitable for :
- People with normal conditions who want to take care of their health. Nutrition is the foundation of health. Monitoring and correcting malnutrition is an important step in maintaining long-term good health.
- People with disorders that may be caused by a lack of micronutrients, which may be found to cause diabetes, fatigue symptoms, mood disorders, poor weight control, osteoporosis, cardiovascular diseases, migraine pain, inability to endure stress, high blood pressure, etc.