What is CPK (Creatine Phosphokinase)?
CPK (Creatine Phosphokinase or Creatine Kinase: CK) is an enzyme, a type of protein that helps facilitate chemical reactions in the body. This enzyme is predominantly found in:
- Skeletal muscles
- Heart muscles
- Lungs
- Brain
When tissues and organs, particularly those listed above, experience injury, inflammation, or cell damage, CPK enzymes are released into the bloodstream in higher-than-normal amounts.
Indications for Testing CPK Levels
When a patient presents with symptoms linked to injury, inflammation, or damage to the heart muscles, skeletal muscles, brain, or lungs, doctors may order a blood test to measure CPK enzyme levels. This test helps in:
- Initial diagnosis of certain diseases.
- Guiding further investigations to identify the underlying causes accurately and promptly.
Doctors may order a CPK test in cases of suspected diseases such as:
- Heart muscle diseases: For example, myocardial infarction (heart attack), often indicated by chest pain.
- Skeletal muscle diseases: Examples include rhabdomyolysis (acute muscle breakdown with symptoms like fever and severe muscle pain) or muscular dystrophy, a condition involving muscle degeneration or weakness.
- Lung diseases: Such as pulmonary embolism, which involves a blood clot obstructing blood flow in the lungs.
- Brain-related conditions: For example, brain oxygen deprivation in cases where the patient has experienced continuous seizures.

Normal CPK Values
- Men: 171 U/L or 2.86 mkat/L (enzyme activity units)
- Women: 145 U/L or 2.42 mkat/L
Conditions That Cause a Mild Increase in CPK Levels
Certain situations can lead to a slight elevation of CPK levels in the blood, including:
- Exercise, particularly intense activities that heavily engage the muscles.
- Medications, such as:
- Steroids
- Certain antibiotics
- Some cholesterol-lowering drugs
- Recreational drugs
- Anesthetics
- Post-surgical recovery
- After intramuscular injections
- Following cardiac catheterization
- Kidney disease: Reduced kidney function impairs the elimination of CPK via urine, causing levels to remain elevated in the blood.
Conditions That Cause a Significant Increase in CPK Levels
Certain conditions or diseases may cause a marked elevation in CPK levels, such as:
- Myocardial infarction (heart attack)
- Rhabdomyolysis (acute muscle breakdown)
- Muscular dystrophy (muscle degeneration)
- Brain hypoxia (oxygen deprivation in the brain)
- Pulmonary embolism (blood clots in the lungs)
Subtypes of CPK:
CPK consists of three enzyme subtypes, which allow for more precise disease diagnosis. However, testing for these subtypes requires advanced technology, available primarily at large hospitals with specialized medical professionals.
The three subtypes of CPK are:
- CPK-1 (CK-BB):
- Found predominantly in the brain and lungs.
- Elevated CPK levels in the blood, along with related symptoms, may indicate conditions such as cerebral ischemia/hypoxia (reduced blood or oxygen flow to the brain) or pulmonary ischemia (e.g., pulmonary embolism).
- CPK-2 (CK-MB):
- Found predominantly in the heart muscle.
- Elevated CPK levels in the blood, along with related symptoms, may indicate myocardial ischemia (e.g., a heart attack).
- CPK-3 (CK-MM):
- Found predominantly in skeletal muscles.
- Elevated CPK levels in the blood, along with related symptoms, may indicate skeletal muscle diseases, such as muscular dystrophy.

Important Notes:
- Elevated CPK levels may indicate muscle inflammation caused by an underlying condition or overlapping factors. Strenuous exercise can also temporarily raise CPK levels. Therefore, doctors may recommend retesting CPK levels after several days of rest.
- If CPK levels remain elevated without recent exercise or other obvious causes, doctors may order additional tests to identify which CPK subtype (isoenzyme) is elevated. This information helps pinpoint the source of damage (skeletal muscles, heart, or brain).
- Certain medications, such as statins, may also increase CPK levels.
Note: Inform your doctor about any medications you are taking.
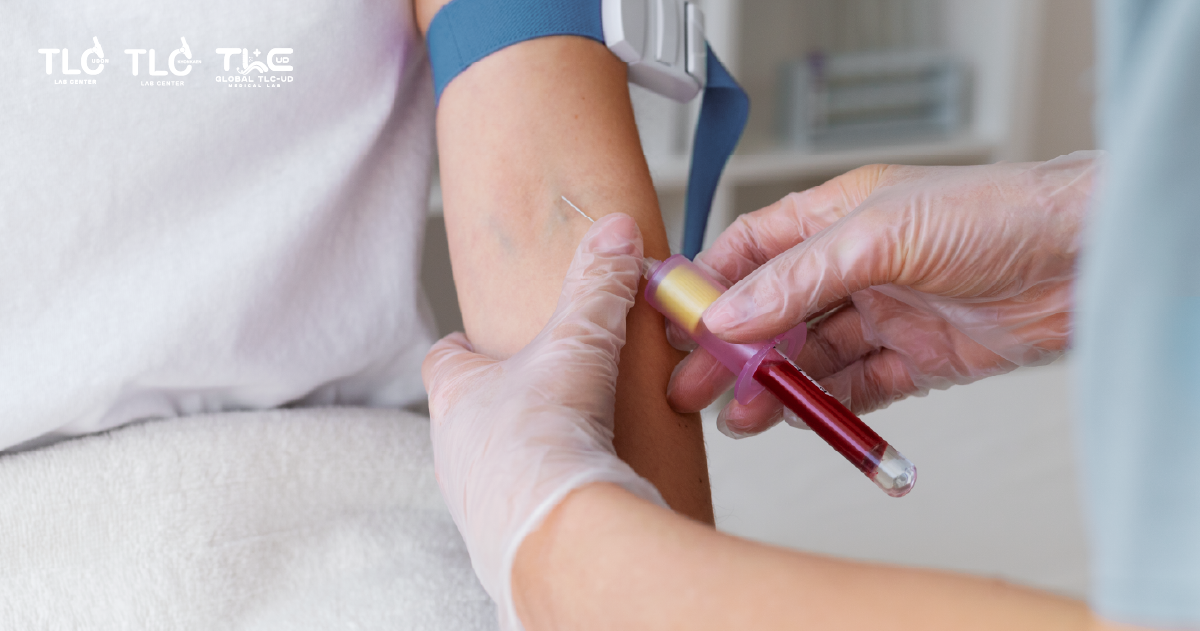
How to Test for CPK Levels
The test involves:
- Blood Sampling:
- A blood test is performed without the need to fast or abstain from food and drinks beforehand.
- Informing the Doctor About:
- Recent activities, such as intense physical exercise.
- Any underlying medical conditions.
- Use of medications in the 2–3 weeks prior to the test.
These factors can influence CPK levels, potentially causing abnormal results.
References:
- emedicine.medscape.com [2020,Feb1]
- healthline.com [2020,Feb1]